Author: Area Bitcoin
Compiled by: Felix, PANews
Summary: Silent Payments can reduce address reuse and enhance overall privacy.
The privacy of Bitcoin transactions is receiving increasing attention. As the demand for more secure and private ways to conduct on-chain transactions grows, a new proposal has emerged: Silent Payments.
This article will explore what Silent Payments are, their importance to the Bitcoin network, and the structure of Silent Payment addresses, among other topics.
What are Silent Payments?
Silent Payments are a method of receiving Bitcoin that does not leak private information, such as your balance or transaction history, to anyone who can see your public address.
This concept originates from a proposal called BIP 352, which suggests using reusable addresses in Bitcoin.
Imagine you want to accept Bitcoin donations or need to receive payments multiple times throughout the year. Currently, you would either need to create a new address for each transaction or reuse the same address, sacrificing privacy and allowing anyone to track all incoming and outgoing records of that address via a blockchain explorer.
However, with Silent Payments, you simply provide a public key address that can be reused without worrying about privacy leaks.
The concept of Silent Payments was first proposed in March 2022. Recently, this BIP was integrated into the official codebase, marking a significant milestone in the development of this technology.
This integration indicates that the technology has undergone sufficient review, and wallet developers can begin implementation, although some minor adjustments may still be needed.
Why is this important?
Bitcoin addresses are currently similar to bank account numbers. However, because the blockchain is completely transparent, anyone can view all transactions associated with an address through a block explorer.
If you reuse the same address, every payment you receive will be public.
Silent Payments change this: you only need to share a public address, and the transaction details are visible only to the sender and receiver. This is achieved through a cryptographic technique that allows the receiver to receive funds to a completely different, unique address each time, and only the receiver can identify and access these funds.
"Silent Payments" is not a completely new idea; it evolved from the concept of "stealth addresses" proposed in 2012.
However, until now, this idea had not been effectively implemented in Bitcoin.
Stealth addresses were mentioned earlier, but what exactly are they?
Stealth Addresses and BIP 47: The Challenges and Limitations in the Pursuit of Privacy
Bitcoin transaction privacy has been a core concern since the network's inception. Over time, various proposals to enhance privacy have emerged, with stealth addresses and BIP 47 being notable, initially proposed by Peter Todd.
The following explores the limitations and challenges these methods face in the pursuit of greater anonymity and transaction efficiency.
Stealth Addresses
Stealth addresses were one of the earliest attempts to improve Bitcoin transaction privacy.
The idea is simple: allow the recipient to generate a unique and private address that only they can access through encryption.
But there was a major obstacle: for the system to work, an additional key needed to be added to the blockchain, typically using the OP_RETURN field.
This presented two serious drawbacks:
-
Loss of Anonymity: Adding extra data to the blockchain makes it obvious that this is a transaction using a stealth address. Any observer can identify this technique, compromising anonymity.
-
Inefficiency and High Cost: Increasing the blockchain data volume makes transactions bulkier, less efficient, and more expensive, contradicting Bitcoin's principle of being lightweight and easily accessible.
An alternative emerged at the time: utilizing an existing key in the transaction to avoid adding extra data.
But due to technical complexity and the lack of efficient tools at the time (e.g., libraries like Lipsack P that simplify these calculations today), this idea was shelved.
BIP 47
Over time, another proposal aimed at solving these issues emerged: BIP 47.
BIP 47 introduced the concept of a notification system instead of adding data to the blockchain with every payment. In this approach, the sender only needs to upload data to the blockchain once, and the receiver can identify this data and use this "key" to simplify future payment processes.
Advantages of BIP 47:
-
Clear Identification for Receiver: The receiver can easily identify which part of the on-chain data is intended for them, making the verification process simpler.
-
Reduced Extra Data: Notification data is only added the first time, saving more space and resources compared to stealth addresses adding data every time.
Disadvantages of BIP 47:
-
More Complex for Sender: Each payment requires the sender to first send an on-chain notification, equivalent to an extra transaction, which becomes very cumbersome at scale.
-
Inefficient Blockchain Usage: The data added for notification is unrelated to the actual payment, considered inefficient.
-
Payment Linkability: If paying the same person multiple times, the receiver might discover the funds come from the same source, compromising anonymity (whereas in Silent Payments the sender is completely anonymous).
-
Identity Exposure: In the notification transaction, the sender's payment code is exposed to the receiver, which can be problematic in situations requiring high anonymity (e.g., donations to sensitive causes).
Although BIP 47 has its advantages (like clarity for the receiver), significant drawbacks such as extra transactions and lack of full anonymity limited its adoption.
Silent Payments aim to address these issues, offering a more intuitive and private user experience. The only disadvantage compared to BIP 47 is the need to scan the blockchain, but this might be a worthwhile trade-off for a significant privacy boost.
In summary, both stealth addresses and BIP 47 contributed to Bitcoin privacy, but their respective limitations hindered widespread adoption.
Silent Payments now emerge as a promising solution, trying to combine the best of both:
-
Strong Privacy
-
High Efficiency
-
Simplified User Experience
How do Silent Payments work?
For the user, the operation is very simple.
Suppose you have a Bitcoin wallet connected to your own node. You generate an SP (Silent Payment) code, which can be shared as a QR code. Anyone who supports Silent Payments can scan the QR code or enter the code to make a payment... it's that simple.
For receivers running a full node, the cost is almost zero due to optimizations that make the process efficient.
However, the recipient has to do a bit more work. The recipient must check every new Taproot transaction on the network to determine if it contains a payment to their Silent Payment address, which requires more processing by the wallet software.
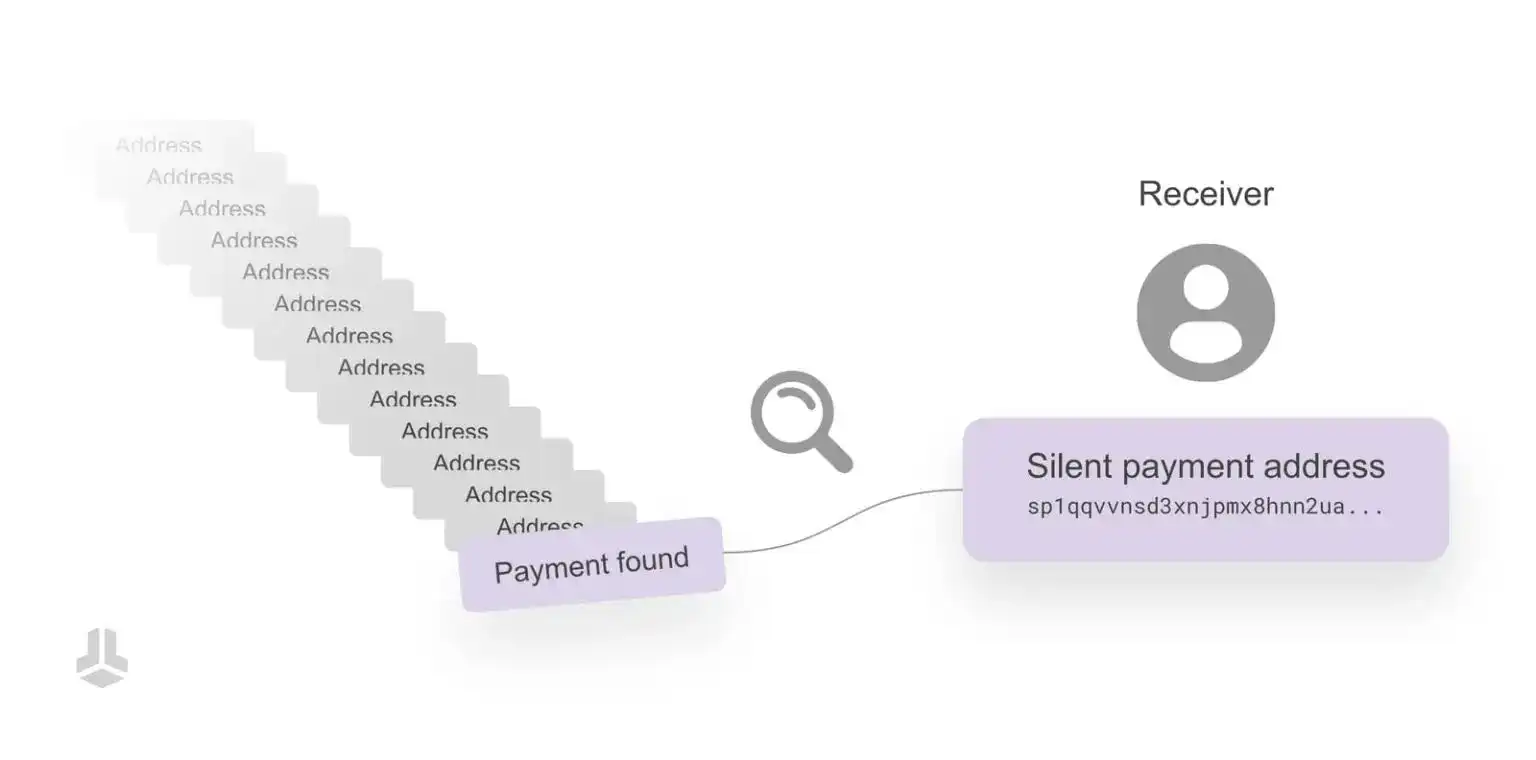
What does a Silent Payment address look like?
The structure of a Silent Payment address is the same as a Taproot address. Taproot addresses use the "bc" prefix, indicating a Bitcoin address, followed by a "1" and a version number, with the rest using bech32m encoding.
Silent Payments also use bech32m encoding, but with the prefix "sp1" (indicating it is a Silent Payment address), and this address contains two public keys. These two public keys do not directly show the destination of the Bitcoin but provide instructions for generating a Taproot public key script.
In practice, users can generate, share, and securely reuse Silent Payment addresses just like a regular Bitcoin address, without sacrificing privacy, which is its core advantage.
Which wallets support this address?
Currently, wallets that support Silent Payment addresses include Cake Wallet and BitBox.
As the Silent Payment feature is still under development and not yet widely adopted, Cake Wallet is one of the first wallets to implement Bitcoin Silent Payments. The wallet is already available in public beta on Android and iOS.
Here's how to use Silent Payments in Cake Wallet:
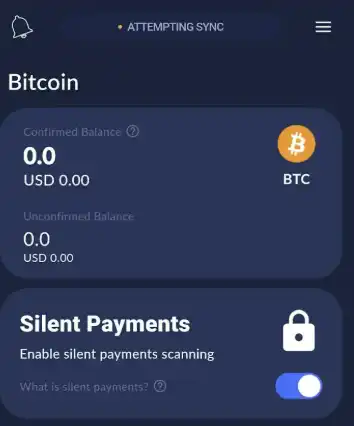
Click the "Silent Payments" button on the card/box on the wallet's main page to start scanning the blockchain for these transactions.
It is important to note that because Silent Payment transactions are anonymous, the wallet must actively scan the blockchain to search for transactions.
Once the scan is complete, Silent Payment verification automatically turns off upon reaching the latest block.
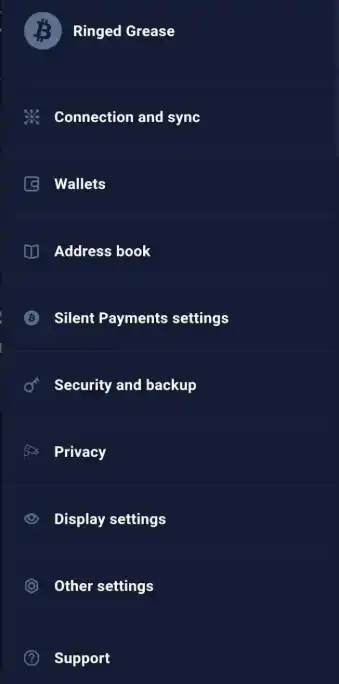
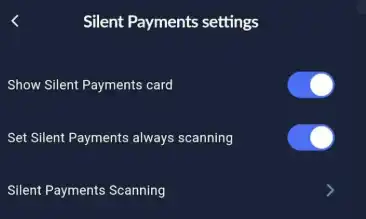
If you want the wallet to continue automatically checking new blocks for Silent Payments, go to "Menu" -> "Silent Payment Settings" and enable the "Always Scan for Silent Payments" option.
BitBox
Like the hot wallet Cake Wallet, BitBox is one of the first hardware wallets to support Silent Payments, greatly enhancing user privacy protection.
Through Silent Payments, the sender can generate a unique address from the receiver's fixed public key. This is particularly useful for activists, NGOs, and charities: they can share a reusable address to receive donations without exposing the identity of the donor or the amount received.
This integration allows BitBox users to support various causes and make payments while avoiding exposing financial activities to unnecessary third parties.
The Role of Labeling
An initial challenge with Silent Payments was how to identify who sent the payment. The solution was the introduction of Labeling.
So, what is Labeling?
Labeling allows you to distinguish between different senders when using a single Silent Payment address, without sacrificing privacy or significantly increasing scanning costs.
This technology allows adding additional information to a Silent Payment address without compromising user privacy. It works by deterministically tweaking the spending key.
Simply put, the spending key is like a digital signature authorizing the use of funds in the address. By tweaking this key slightly, different payment sources can be identified.
For example, suppose you have two Silent Payment addresses:
-
One for activity on X
-
Another for activity on Nostr
With labeling, the first half of these two addresses is the same (indicating they both belong to you), but the second half is slightly different, helping you identify the source of the payment.
This way, when viewing your funds, you can see that some payments came from X users and some from Nostr.
This flexibility strikes a balance between protecting privacy and collecting useful transaction information.
Of course, if you want complete anonymity, you can also just use a standard Silent Payment address without labels, ensuring the sender has no identifiable information. But if you need to track the source of payments, labeling provides an efficient way.
This technology can be applied to various scenarios such as exchanges, social media platforms, personal use, allowing you to manage multiple online identities without creating obvious links, or simply to get more payment information when needed.
Exchange Silent Payment Example
Interesting application scenarios would emerge if exchanges adopted this technology.
Suppose you deposit funds into an exchange. With Silent Payments, instead of giving you a reusable deposit address, the exchange generates a Silent Payment address for you.
Every time you send a payment to this address, the exchange can automatically identify it as yours (through the labeling mechanism), without you having to manage multiple addresses. Furthermore, this technology is also very useful for automatic withdrawals.
You can reuse the same Silent Payment address across platforms without managing different extended public keys (xPubs) for each platform, greatly simplifying the process.
Conclusion
Silent Payments have the potential to revolutionize the way Bitcoin is used, offering a simpler, more intuitive experience while significantly enhancing privacy.
If this technology is widely adopted, the rate of on-chain address reuse could drop significantly, thereby creating a safer and more private environment for everyone.
Silent Payments provide a great opportunity to align user incentives with best privacy practices, making future Bitcoin payments more covert and secure than ever before.
Related reading: Over 1.7 million BTC potentially under direct attack? Bitcoin faces quantum controversy again, public chains begin defense battle