Amid the global wave of digital currencies, Singapore is emerging as the "overseas hub" for international crypto institutions. Whether it's stablecoin issuance, digital asset trading, or institutional-grade custody and payment clearing, global fintech companies are seeking compliant and stable landing paths here.
Behind this lies a systematic regulatory framework established by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): a clear legal framework, a complete licensing system, and a regulatory philosophy that balances risk and innovation, setting Singapore apart from major jurisdictions worldwide. Unlike the fragmented regulatory environment in the United States and the high compliance costs in Europe, Singapore offers a predictable and actionable compliance path.
This series of reports will systematically interpret Singapore's digital asset ecosystem from five dimensions: regulatory framework, licensed institutions, financial institution practices, international cooperation, and institutional advantages, showing how its system attracts global institutions while providing a reference for the Asia-Pacific and global markets.
Regulatory Framework and Main Licensing System
(I) Core Regulatory Authority
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is the unified regulatory authority for Singapore's digital asset and financial markets, fully responsible for overseeing the payment system, digital currencies, fintech, and related financial services. MAS implements a management model combining functional regulation and risk-oriented regulation for digital asset activities through a combination of legislation and a licensing system.
(II) Regulatory Laws and Overall Framework
1. Payment Services Act (PSA)
The Payment Services Act is the foundational legal framework for digital asset regulation in Singapore. The act defines digital currencies/cryptocurrencies as "Digital Payment Tokens (DPTs)" and brings related services such as payment, exchange, transfer, and custody into the payment services regulatory system.
The act specifies the following core requirements:
- Digital payment token services require a license to operate;
- Sets Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) obligations;
- Defines compliance standards such as capital adequacy, customer asset segregation, and risk management;
- Ensures financial stability and consumer protection through ongoing supervision.
2. Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA)
The Financial Services and Markets Act further expands Singapore's regulatory boundaries for digital asset activities on the basis of the PSA. Unlike the PSA, which primarily regulates "services provided to local Singaporean clients," the FSMA extends its regulatory scope to all institutions registered in Singapore or with a place of business there, which use Singapore as an operational base to conduct digital asset-related business, even if their service targets are located overseas. Specifically, any activity involving the issuance, trading, matching, custody, or related services of digital currencies through a Singapore entity falls under the FSMA's regulatory purview.
The act will officially take effect from 2025. MAS has clearly stated that any institution established in Singapore but providing digital asset services only to overseas clients must obtain the corresponding license within the specified period, otherwise face hefty fines or even criminal liability, plugging the regulatory gap of using Singapore as an "offshore channel" at the institutional level.
(III) License Types and Regulatory Division
Currently, the core licenses for the crypto asset field in Singapore mainly include the DPT (Digital Payment Token Service) license under the Payment Services Act and the DTSP (Digital Token Service Provider) license.
1. Licenses under the Payment Services Act (DPT System)
According to the Payment Services Act, entities involved in digital payments, remittances, e-money, or cryptocurrency services need one of the following licenses:
(1) Standard Payment Institution (SPI) License – applicable to smaller-scale payment service providers;
(2) Major Payment Institution (MPI) License – applicable to institutions with larger transaction volumes, involving cross-border payments or digital asset services.
It is particularly important to note that currently, only MPI license holders are permitted to conduct Digital Payment Token (DPT) related business; SPI license holders have not yet been granted this permission.
Therefore, the so-called "DPT license" in the industry essentially refers to an MPI license that includes the scope of digital payment token services.
2. DTSP License (Digital Token Service Provider)
According to the Financial Services and Markets Act, entities without a DTSP license are prohibited from providing any digital token-related services to overseas clients through their business premises in Singapore. The DTSP license primarily targets digital asset institutions that provide "external services," and its regulatory scope is broader than the DPT system, with more stringent compliance requirements.
After the implementation of the new DTSP policy, Singapore systematically cleaned up crypto enterprises characterized by "establishing a local entity but lacking substantive operations." Except for a few institutions with genuine business and compliance capabilities, most non-compliant enterprises were required to cease relevant operations or relocate their entities away from Singapore by June 30, 2025, effectively resulting in a round of regulatory clearance.
According to industry analysis, institutions already under the following regulatory frameworks typically do not need to apply for a separate DTSP license:
(1) Already hold a license under the Payment Services Act;
(2) Have obtained an exemption under the Payment Services Act;
(3) Already hold a relevant license under the Securities and Futures Act or the Financial Advisers Act.
It should also be noted that what is often referred to in media reports as "DTSP licensed institutions" corresponds, in MAS's public information system, mostly to "MPI license holders including digital payment token services," rather than independently published DTSP license holders.
To date, MAS has not publicly released a complete list of DTSP license holders; related information is primarily reflected through regulatory documents and policy statements.
Singapore's Digital Asset Licensing System
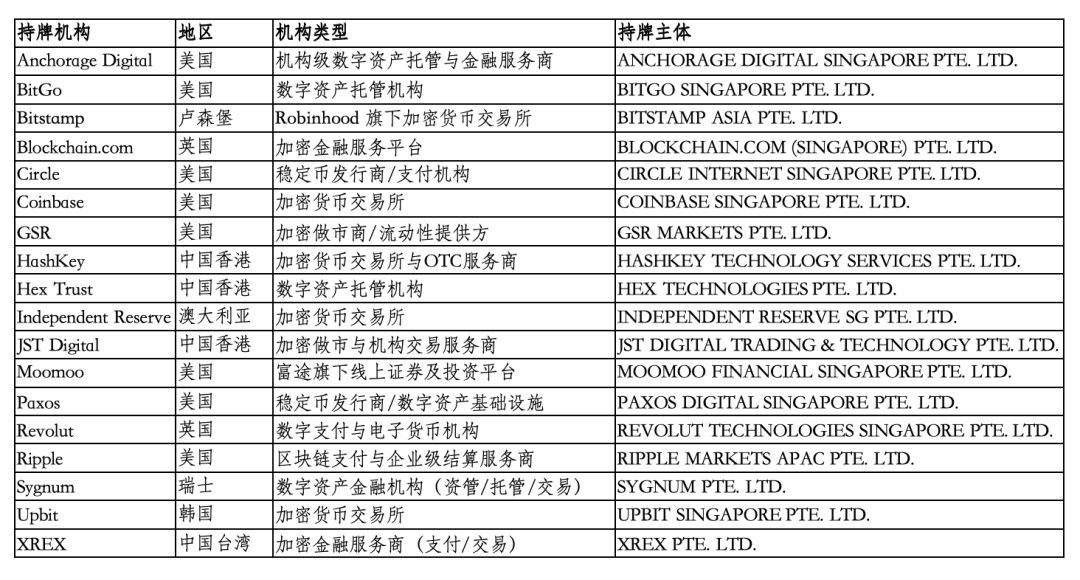
As of the writing date, MAS has issued MPI licenses including the Digital Payment Token Service business scope to 36 institutions with international backgrounds.
In terms of the composition of licensed entities, although some institutions have US or other overseas backgrounds, or are controlled by multinational groups, they must use a locally registered legal entity as the licensed entity when conducting related business in Singapore. Relevant compliance obligations, regulatory responsibilities, and business scopes are all borne by this Singapore entity to MAS in accordance with the Payment Services Act, reflecting Singapore's consistent regulatory principle of "territorial regulation, entity responsibility."
(I) MPI Licensing/Exemption Status of Global Institutions
1. Licensed (Listed in A-Z order)
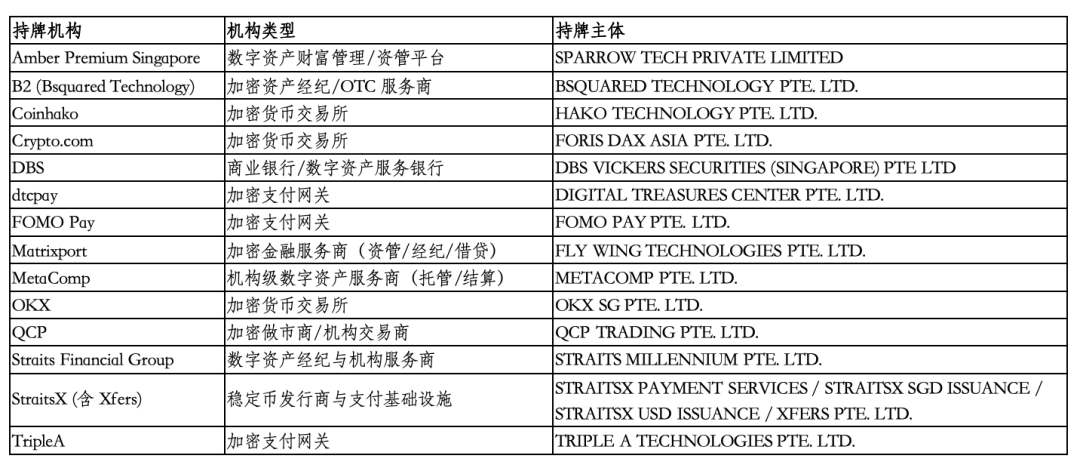
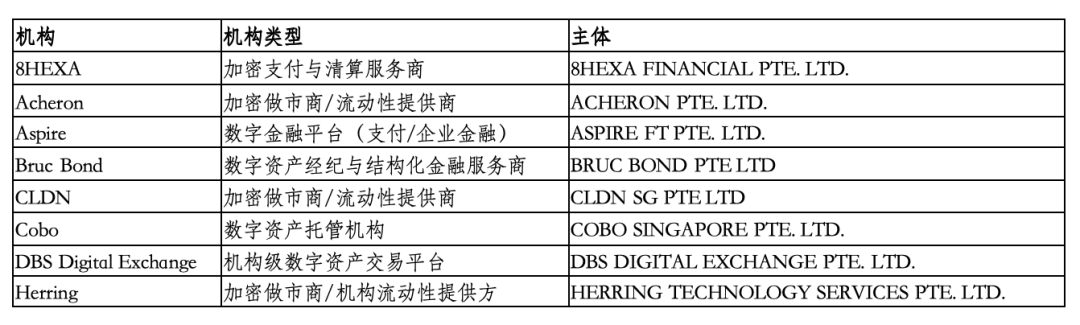
2. Exempted (Listed in A-Z order)
3. Unique Business Developments
- In December 2025, Coinbase launched a prediction market feature in the US, not applicable to Singapore users.
- In November 2024, Paxos Singapore and DBS Bank issued the USDG dollar stablecoin.
(II) MPI Licensing/Exemption Status of Local Singapore Institutions
1. Licensed (Listed in A-Z order)
2. Exempted (Listed in A-Z order)
3. Unique Business Developments
In December 2025, the cryptocurrency platform Crypto.com announced a cooperation with the local largest bank, DBS Group, to enhance fiat currency payment functions, enabling local users to more conveniently use SGD and USD deposit and withdrawal services. In the same month, StraitX announced plans to launch its Singapore dollar stablecoin XSGD (issued in 2020) and US dollar stablecoin XUSD on the Solana public chain in early 2026.
- In November 2025, Grab and StraitsX developed a digital wallet supporting stablecoins.
- In September 2025, OKX Singapore launched a stablecoin payment function for GrabPay merchants.
- In August 2025, Singapore's DBS Bank launched tokenized structured notes on Ethereum. In the same month, Volkswagen Singapore cooperated with FOMO Pay to support digital currency payments.
So far, we have梳理了 (sorted out) Singapore's digital currency regulatory framework, core laws, and licensing system, and also understood the composition of licensed institutions and market structure. It can be seen that Singapore is not simply "crypto-friendly"; rather, it has built a robust and attractive digital asset ecosystem through clear systems and strict license management.
In the next part, we will delve deeper into how local financial institutions participate in digital asset practices, international cooperation and innovation trends, and the practical significance of Singapore's system for global institutions.
*This content is for reference only and does not constitute investment advice. The market carries risks, and investment requires caution.