Article Authors: May P, Janus R
Article Source: CoinFound
About CoinFound: CoinFound is a TradFi Crypto data technology company for institutional and professional investors, providing RWA asset data terminals, RWA asset ratings, Web3 risk relationship graphs, AI analysis tools, and customized data services. From data integration and risk identification to decision support, it helps institutions obtain critical intelligence and convert it into actionable insights at lower costs and higher efficiency, building the global RWA infrastructure.
Takeaway
- USDT Rating Downgrade and Controversy: The proportion of non-pegged assets (BTC, gold, etc.) in USDT's reserves has reached about 24%, coupled with insufficient governance and transparency, making it perceived as higher risk under the traditional financial framework, leading to the rating downgrade. The downgrade of USDT's rating has sparked controversy.
- Tether Significantly Increases Gold and Bitcoin Proportion: For purposes such as inflation hedging, asset diversification, reducing single exposure to the US dollar, and enhancing returns, Tether has been continuously increasing the proportion of gold and Bitcoin reserves in recent years.
- The Essence of the S&P and Tether Disagreement: Traditional financial risk perception prioritizes 'solvency,' focusing on 'the ability to liquidate reserves under extreme redemption pressure'; whereas Tether focuses on 'market liquidity priority' and long-term value preservation and risk resistance (especially inflation risk). Their dimensions for measuring risk are completely different.
- Strategic Intent Behind Tether's Reserve Transformation: Tether's reserve model is shifting from a '1:1' cash-equivalent reserve to a hybrid model of 'hard assets (gold) + digital assets (BTC) + low-risk assets (US Treasuries)'. Essentially, this is a transformation from a 'stablecoin issuer' to a 'global liquidity provider + digital asset reserve institution,' driven by core factors including inflation hedging needs, pro-cyclical yield enhancement (e.g., the predicted BTC/gold bull market in 2025), and de-dollarization strategy. In fact, Tether is becoming more like a 'shadow central bank' rather than a simple stablecoin issuer.
- Limitations of the Current Rating System: S&P's 'stability rating' covers 'redemption risk' but cannot address investor demands for Tether's 'asset appreciation capability' and 'cyclical resilience.' The market may require more multi-dimensional risk rating information in the future. Additionally, a dual-framework model of 'Stability Rating (Regulatory + Solvency) + Investment Risk Rating (Return + Cycle)' might be needed to bridge the risk perceptions of traditional and crypto finance.
- USDT's Short-Term Risks and Long-Term Trends: USDT's peg stability is still supported by on-chain liquidity. However, in the short term, the 24% high-volatility assets (BTC/gold/loans) in the reserves may expose risks during the 2026 interest rate cut cycle and a potential crypto bear market (Tether's books showed huge unrealized gains in 2025 from holding gold and Bitcoin reserves; however, the situation may change in 2026). In the long term, the 'central bank-ization' trend of stablecoins (anti-inflation assets + global network + energy) will drive the industry towards 'transparency + standardization'.
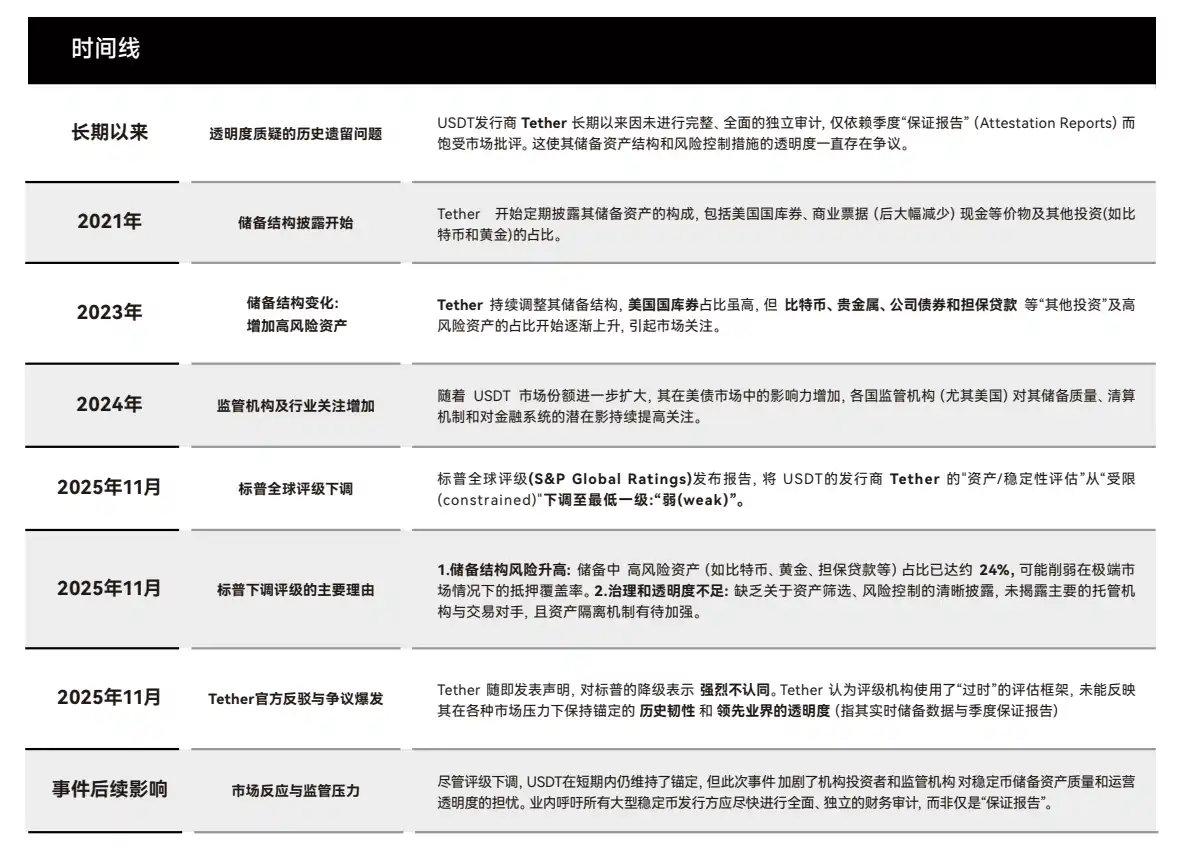
1. Event Recap: The Controversy and Essence of S&P Downgrading USDT's Rating
1.1 Event Timeline and Core Contradiction
In November 2025, S&P Global downgraded USDT's 'Asset/Stability Assessment' from 'constrained' to 'weak', with two core reasons:
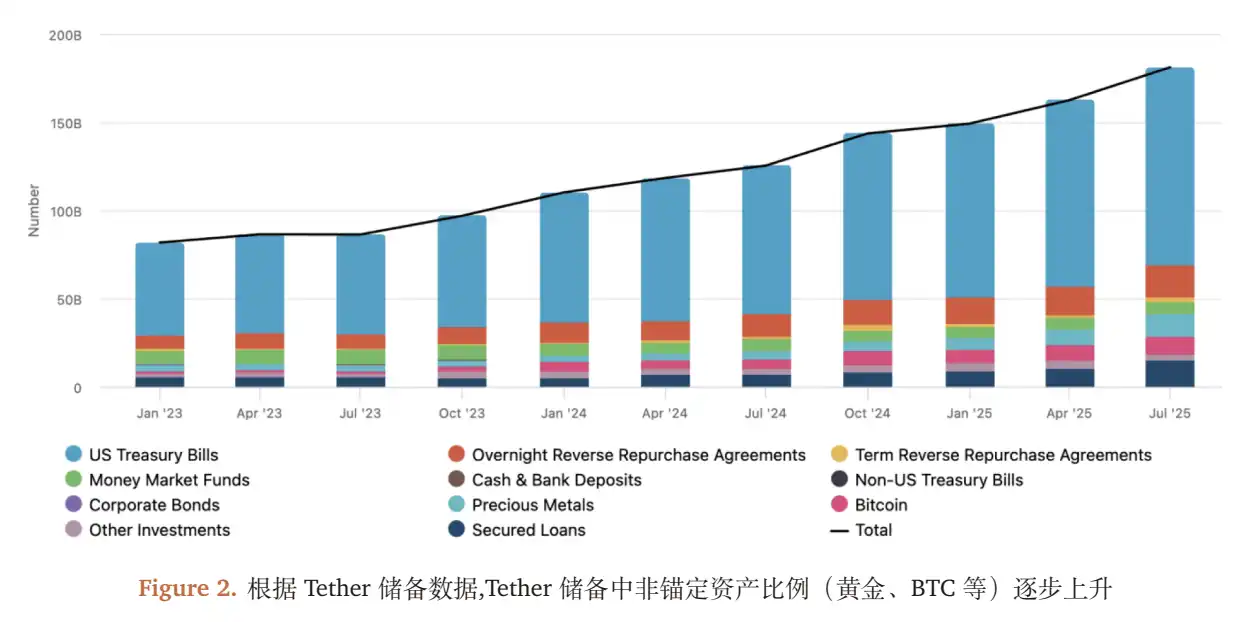
- Reserve Structure Risk: High-volatility assets (BTC, gold, loans, etc.) in Tether's reserves have reached 24% (only 12% in 2023). Such assets cannot be liquidated quickly in a 'panic redemption' scenario.
- Insufficient Governance Transparency: Failure to disclose major custodians, details of on-chain collateral segregation mechanisms, and providing only 'quarterly Assurance Reports' instead of full independent audits.
Tether's counterattack focused on 'actual market performance' and questioned the rating methodology from the traditional financial system:
- Historical Resilience: USDT maintained its peg through 8 extreme events including the 2022 FTX collapse, the 2023 Silicon Valley Bank crisis, and the 2024 crypto regulatory tightening.
- Leading Transparency: Since 2021, providing 'real-time reserve data' (verifiable via on-chain addresses), with Quarterly Assurance Reports covering over 95% of assets, superior to some traditional money market funds.
(Chart 1: USDT Rating Downgrade Event Recap)
1.2 The Essence of the Disagreement: Clash of Two Risk Measurement Systems
In November 2025, S&P Global Ratings downgraded USDT's stability assessment to the lowest level, 'weak'. Tether publicly countered, accusing S&P of 'using an old-world framework' and ignoring the multiple extreme stress tests USDT has withstood over the past decade. This debate is not just a rating controversy but a head-on collision of two financial civilizations.
- S&P represents: The 'Regulation - Capital Adequacy - Solvency' system.
- Tether represents: The 'Market Liquidity - Global Trading Demand - On-chain Instant Settlement' system.
- These two measure risk in fundamentally different ways, thus destined to fail to reach consensus. The argument between S&P and Tether,表面上 is a war of words over a 'stability rating,' but本质上 reflects completely different understandings of risk from two different worlds.
- S&P and Tether: one from 100 years of traditional finance, one from 10 years of on-chain high-frequency markets. S&P uses the logic of 'central bank — bank — money market fund'; Tether relies on the logic of 'on-chain liquidity — perpetual leverage — insurance fund — automatic liquidation.'
And the logic represented by Tether is currently unavailable to traditional financial markets.
1.3 What S&P Sees: The Redemption Logic of Traditional Finance
In the cognitive framework of traditional finance, all 'instruments promising 1:1 redemption' (money market funds, commercial banks, stablecoins) must meet two hard conditions:
1. Reserve assets must be highly safe and immediately liquidatable: S&P noted in its report: Tether's reserves in BTC, gold, and loan-type assets exceed 20%. These assets are volatile and have long liquidation cycles, potentially impossible to sell quickly at face value in a 'panic redemption' scenario.
2. Governance structure must be transparent, custody arrangements must be penetrable: S&P believes Tether's custodian information, on-chain collateral segregation, and risk disclosure are still insufficient.
That is, in S&P's world: The key risk of a 'stablecoin' lies in whether it can withstand the moment when everyone comes to redeem at once? This is the redeemability stability of the traditional system.
1.4 What Tether Insists On: The Liquidity Logic of the Crypto World
If TradFi's stability comes from 'are the reserves enough, fast enough, safe enough?', then Tether's stability comes from 'can I maintain huge liquidity on-chain, can perpetual market risks be absorbed, can the secondary market maintain the price peg?' In other words:
- TradFi measures stability as redemption ability, while Crypto measures stability as market liquidity + settlement stability.
- And Tether's ten-year record (including multiple panic markets) indeed shows: USDT's de-pegging is often not due to 'insufficient reserves,' but due to 'temporary imbalance in secondary market liquidity,' which has been quickly repaired each time.
Why does Tether strongly counterattack? Because it adheres to another 'market logic.' Tether's response emphasizes three points:
1. USDT has maintained a 1:1 peg under all extreme sentiments: Including multiple crypto exchange collapses, the Fed's rapid rate hike cycle, regulatory tightening, bank run events, etc. From Tether's perspective, 'I am not theoretically stable, but practically stable after ten years of operation without de-pegging. The real rating of a stablecoin is given by the market daily, not by models.'
2. Real-time reserve data + Quarterly attestation reports are sufficiently transparent: Tether believes it is already superior to some shadow banks or MMFs in TradFi. But S&P does not recognize the form of 'real-time web disclosure' because S&P's methodology distinguishes between 'unaudited transparency and credible transparency.'
3. BTC/Gold are 'anti-inflation assets + strategic reserves', not high-risk exposure: The surge in BTC and gold prices in 2025 gave Tether huge paper profits (over $10 billion). This has effectively made Tether adopt a hybrid central bank-style model of 'hard assets + US Treasuries + loans + digital assets.' Tether's worldview is 'I am like a national central bank's reserves, my structure is not the traditional dollar system, but a new global asset basket.' But S&P's worldview is 'You are not a central bank, you are just a token issuer promising 1:1 redemption.'
1.5 Why Do the Two Sides Have Completely Conflicting Understandings of 'Risk'?
It reveals a key fact: The logic of risk-bearing is completely different between the crypto market and TradFi.
- Arthur Hayes published an article on perpetual contracts on November 27th. Perpetual contracts are a typical example that fully illustrates the current inability of traditional finance and crypto finance to merge. In traditional finance (TradFi), the risk of forward contracts comes from 'unlimited margin call liability.' In TradFi, untimely liquidation, position bankruptcy, investors losing more than their margin (negative equity) require additional funds (Margin Call), even potentially using all personal assets to repay debts. Therefore, TradFi must require reserves of 'extremely high-quality assets,' tolerating no volatility.
- But in crypto finance (Crypto), risk is borne by 'insurance funds + automatic liquidation + ADL (Auto-Deleveraging).' This is because in crypto perpetual contracts, losses are not the trader's unlimited liability. In the crypto finance system, liquidation surpluses replenish the insurance fund, liquidation fees inject into the insurance fund, ADL acts as a backstop, and exchange自有 funds supplement. The final result is that crypto users at most lose their margin but do not owe debt. Therefore, the crypto market can accept high-volatility assets more easily because the market structure provides a backstop.
This is the essence of the S&P and Tether分歧: S&P measures TradFi risk, i.e., 'If everyone comes to redeem, can you pay out?' Tether deals with Crypto risk, i.e., in a 7x24 high-volatility market, can I guarantee trading, liquidity, and global high-frequency usage? They are not measuring the same dimension.
2. Tether's Reserve Transformation: The Strategic Logic from 'Stablecoin' to 'Shadow Central Bank'
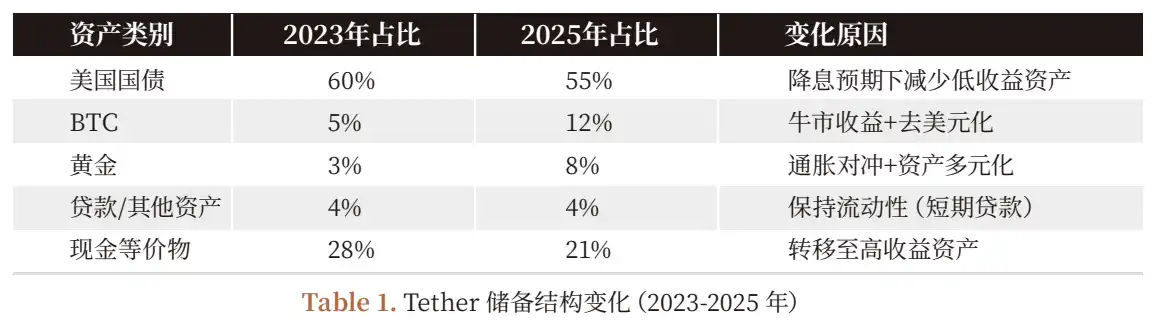
2.1 Time Series Changes in Reserve Structure (2023-2025)
2.2 Why Increase BTC and Gold Proportion? Balancing Pro-Cyclical Returns and Long-Term Strategy
Tether's reserve structure transformation (2023-2025) is not random but a triple consideration of 'return - risk - strategy':
1. Inflation Hedging Demand: Fed rate hikes from 2022-2024 led to a decline in the US dollar's purchasing power (US CPI rose from 2% to 8%), making gold (traditional inflation hedge) and BTC (digital gold) core assets for hedging inflation;
2. Pro-Cyclical Yield Enhancement: In 2025, BTC price rose from $40k to $65k (up 62.5%), gold rose from $1900/oz to $2500/oz (up 31.6%). Tether'sunrealized gains accounted for 70% of the net profit in the first nine months of 2025 ($10 billion) (Treasury interest contributed only $3 billion);
3. De-Dollarization Strategy: The proportion of US dollar reserves in Tether dropped from 75% in 2023 to 55% in 2025. By increasing the proportion of gold and BTC, it reduces exposure to the single asset of the US dollar (responding to the US debt ceiling crisis, global de-dollarization trend).
2.3 The 'Sweetness and Hidden Danger' of the Profit Structure: Risks Under the Pro-Cyclical Trend
Tether's 2025 performance (net profit exceeding $10B in the first nine months) seems brilliant, but its profit structure highly depends on the 'bull market cycle':
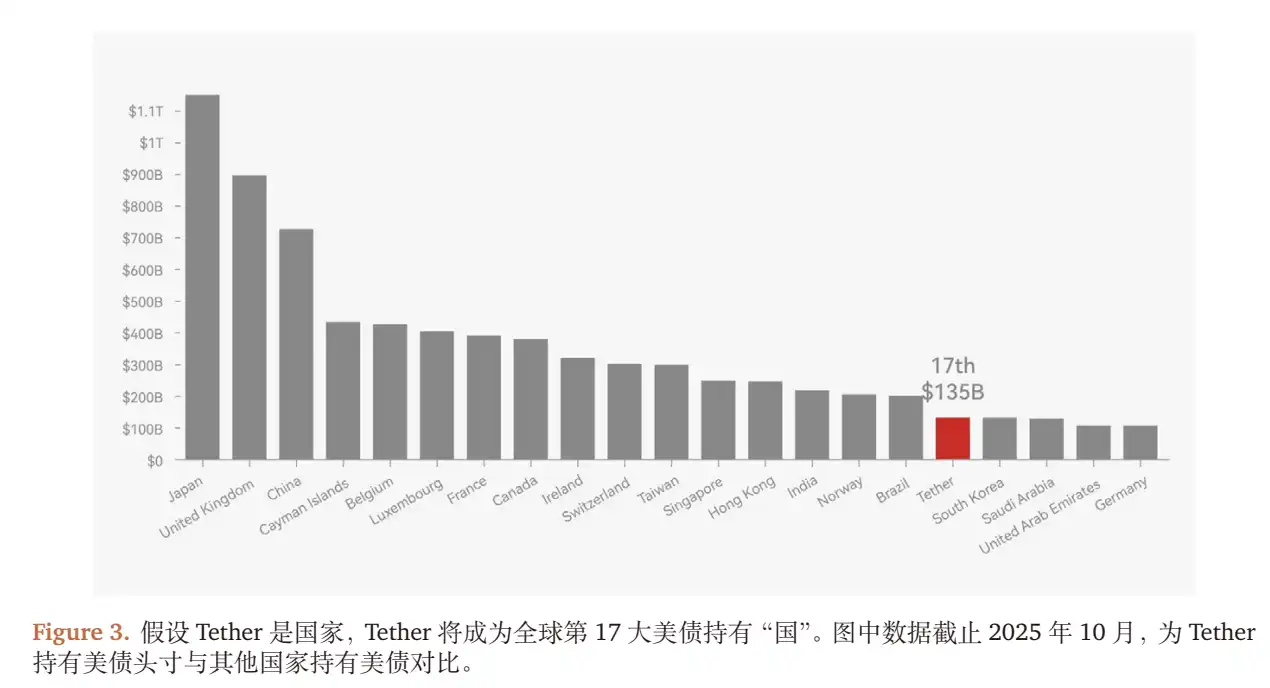
- Stable Income: Interest income from approximately $135 billion in US Treasuries (1-year Treasury yield about 2.2% in 2025), contributing about $3 billion;
- Floating Income: Unrealized gains from BTC (approx. 100k coins) and gold (approx. 10 million ounces), contributing about $7 billion (corresponding to a BTC rise of $25k/coin, gold rise of $600/oz).
Risk Transmission Mechanism:
- If the Fed cuts rates by 25bp in 2026 (market consensus), Tether's Treasury interest income willdecrease by $337.5 million per year ($135B * 0.25%);
- If BTC price falls 20% (back to $52k), gold falls 10% (back to $2250/oz), Tether's unrealized gains willshrink by approximately $2.5 billion (BTC impairment ~$2.5B? Calculation based on provided numbers might differ: 100k BTC * $13k drop = $1.3B? 10M oz Gold * $250 drop = $2.5B. Total ~$3.8B? The original text says 25亿美元缩水. Assuming original numbers are estimates.);
- If the crypto market enters a bear market (like 2022), stablecoin issuance contracts (USDT issuance dropped from $80B to $60B in 2022), Tether's Treasury holdings规模 will decrease, further compressing interest income.
2.4 The Ultimate Goal of Strategic Transformation: From 'Stablecoin' to 'Shadow Central Bank'
By tracking Tether's on-chain addresses and business布局, we find it has surpassed the定位 of a 'stablecoin issuer' and is building a 'shadow central bank' system of 'anti-inflation asset reserves + global stablecoin issuance + on-chain distribution network + energy':
- Anti-Inflation Asset Reserves: BTC, gold占比 24%, corresponding to 'central bank's foreign exchange reserves';
- Global Stablecoin Issuance: USDT's on-chain trading volume in 150 countries accounts for 70% of the total stablecoin trading volume, corresponding to 'central bank's currency issuance';
- On-Chain Distribution Network: Cooperating with 200+ exchanges/DeFi protocols like Binance, Uniswap, enabling global instant transfers of USDT;
- Energy Layout: Investing $1 billion in Bitcoin mining farms (accounting for 5% of global算力 in 2025), hedging the energy costs of BTC mining.
2.5 Market Performance: USDT's Peg Stability and Liquidity
- Peg Deviation: From 2023-2025, USDT's price deviation (spread against the US dollar) averaged only 0.02%, far lower than USDC (0.05%) and DAI (0.1%);
- On-Chain Liquidity: The liquidity pool size of USDT on Uniswap V3 reached $5 billion? (Original text says 50$ 亿美元, likely $5B or $50B? 2023 was only $1B), market maker quote spread (Spread) stabilized within 0.01%;
- Institutional Holdings: The proportion of institutions holding USDT increased from 15% in 2023 to 30% in 2025, indicating that institutions already regard USDT as a 'portfolio tool combining liquidity and asset appreciation (rather than a pure stablecoin).
3. Future Outlook: The Evolution Direction of Stablecoin Rating Systems
3.1 Limitations of the Current Rating System: Only Covers Redemption Risk
S&P's stability rating addresses the question ofwhether the stablecoin can be redeemed, but cannot respond to the core needs of institutional investors:
- Quality of Earnings: Is Tether's profit sustainable? (e.g., declining收益 after Treasury rate cuts)
- Exposure Risk: Is the proportion of BTC and gold too high? (e.g., impact of a 20% drop in BTC on reserves)
- Operational Risk: Is Tether's governance transparent? (e.g., security of custodied assets)
3.2 Beyond the Current Rating System
In the future, the crypto market may need a more comprehensive rating system, not just focusing on redemption and stability. The future rating design might be as follows:
Stability Rating (Upgrade of existing framework)
- Core Metrics: Reserve assets' 'Safety Coefficient' (cash equivalent ratio), 'Liquidity Coefficient' (liquidation cycle of high-volatility assets), 'Transparency Coefficient' (independent audit coverage, custody information disclosure);
- Goal: Answer the question 'Can the stablecoin maintain redemption under extreme挤兑?'
Investment Risk Rating (New framework)
Core Metrics:
- Earnings Quality: Proportion of stable income (Treasury interest) (>=50% is 'low risk');
- Exposure Management: Proportion of high-volatility assets (<=10% is 'low risk');
- Operational Risk: Profit growth rate of the issuer (>=10% is 'stable'), regulatory compliance (e.g., US MSB license, EU MiCA certification);
- Goal: Answer the question 'Can the stablecoin issuer operate sustainably, and can its reserve assets appreciate?'
3.3 Industry Trend: From 'Controversy' to 'Standard'
This controversy between S&P and Tether is essentially the 'rule export' from traditional finance to the crypto market. We judge:
- Short Term: Regulation will promote 'mandatory transparency requirements' for stablecoins (e.g., the US Stablecoin Bill requiring 100% cash-equivalent reserves, EU MiCA requiring full audits);
- Medium Term: The rating system will develop further, and ratings will not be limited to the 'regulation - capital adequacy - solvency' system. Institutional investors will choose stablecoins based on 'Stability Rating + Investment Risk Rating' for different scenarios;
- Long Term: Stablecoins may further differentiate into 'pure stability tools' (e.g., USDC, 100% cash equivalents) and 'stability tools with appreciation' (e.g., USDT, hybrid reserves), meeting the needs of different investors.
Risk Warning
1. Reserve Asset Price Volatility Risk: A drop in BTC and gold prices will lead to impairment of Tether's reserves, affecting redemption confidence;
2. Regulatory Policy Risk: If the US and EU require stablecoins to hold 100% cash equivalents, Tether will need to sell BTC and gold, causing profits to plummet;
3. Market Liquidity Risk: In extreme market conditions (e.g., 2022 FTX collapse), on-chain liquidity drying up may cause USDT to de-peg;
4. Operational Management Risk: Tether's lack of governance transparency may trigger internal operational risks (e.g., custodied assets being stolen).
《USDT Rating Controversy》Research Report Download Link:https://app.coinfound.org/research/1
Analyst Statement: This report is based on public information and reasonable assumptions and does not constitute investment advice. The analyst does not hold positions in Tether or USDT.
Copyright Statement: The copyright of this report belongs to Coinfound.