Author: Lex Sokolin
Original Title: Analysis: Stripe's Tempo is building the Apple of payment blockchains
Compiled and Edited by: BitpushNews
So fast!
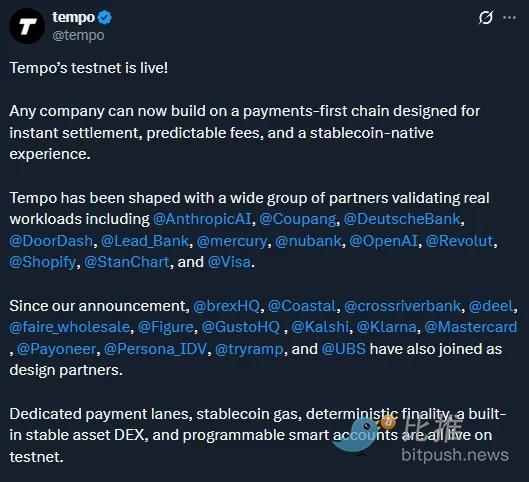
Stripe's controversial payment chain—forked from Ethereum and modified with key adaptations for fintech applications—is now live on the testnet.
It's worth noting that the project has completed a seed funding round of $500 million, co-supported by Stripe and Paradigm, targeting the payment industry as its initial market entry point.
(Source Chart: Technical Architecture Comparison Diagram)
Interested parties can check out the code repository here.
The first thing we noticed is that the technology is released under the Apache or MIT open-source licenses. This is good news.
The Apache 2.0 license is a popular permissive open-source license from the Apache Software Foundation, allowing broad commercial use, modification, and distribution, requiring only the retention of copyright notices, provision of the license text, and notation of significant modifications, while also including an explicit patent grant from contributors to users.
Therefore, the open-source community is free to adopt any of Tempo's technological achievements. This means that although Ethereum may not gain the commercial landing advantages that Tempo brings to Stripe, it can still absorb its protocol-level technological innovations.
So what are the key differences? We quote the core design notes:
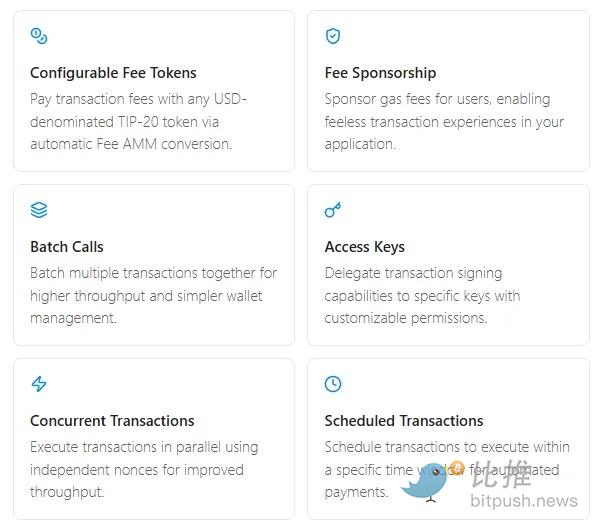
Payment Channels Reserved for TIP‐20 Transfers
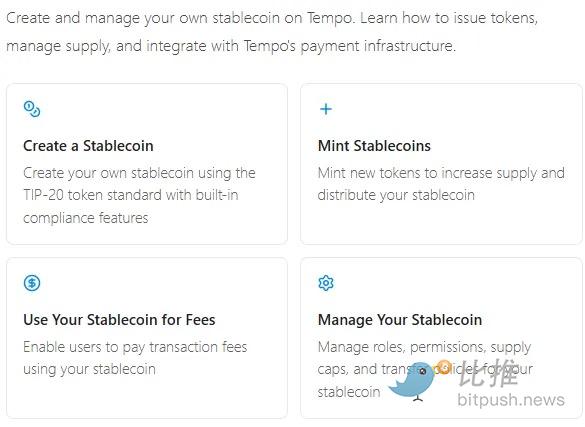
TIP‐20 is a stablecoin issuance standard created with specific functions. Its core effect is to bundle stablecoin issuance with prioritized transfers on-chain.
On Ethereum, different stablecoin issuers compete with each other, and these issuers are not fundamentally different from other token issuers.
On Tempo, the stablecoin issuance contract is solidified in the TIP20Factory, creating the potential for future on-chain revenue. Establishing a fast lane for such tokens gives them a permanent advantage. However, anyone can use this factory contract, meaning competition still exists at the distribution level, but manufacturing tends to be centralized.
Low, Predictable Fees Paid in Stablecoins
Users can pay Gas fees directly with USD stablecoins upon initiation. A fee automated market maker (AMM) will convert them into the validator's preferred stablecoin. The target cost for TIP‐20 transfers is less than one-thousandth of a dollar (<$0.001). Liquidity providers in the AMM can earn a 0.3% fee from each swap. This design also avoids Miner Extractable Value (MEV) and arbitrage attacks against transactions—which have cost users over $1 billion on Ethereum.
Generalizing the way users pay for transactions is a commendable design direction, and Tempo achieves multi-directional payment options.
Here, any asset can be converted into stablecoins to pay for Gas; on Ethereum, while any asset (including stablecoins) can also be converted to ETH to pay Gas, this process is not automated and requires support from smart accounts.
More importantly, Ethereum has execution competition between different AMMs, rather than solidifying a specific AMM within the chain mechanism. This competition is crucial when trying to spur innovation for new financial primitives; but for Tempo, which aims to industrialize financial primitives, its importance is relatively lower.
Native Smart Account Integration
Tempo integrates the excellent concept of smart accounts into transactions: (1) supports batch processing of multiple operations (payroll, settlement, refunds); (2) a fee sponsorship mechanism, allowing applications to pay Gas on behalf of users; (3) scheduled payment functionality, supporting recurring and timed payments within protocol-level time windows; (4) modern authentication methods using passkeys (e.g., biometric login).
(Attached Figure: Statista chart of long-term competitive trends between Microsoft and Apple)
Just as Stripe itself integrates various fintech services into a single platform, Tempo is absorbing the most demanded payment features as native parts of the chain, rather than leaving them to third-party development and competing for user awareness. This is the Apple-style software development philosophy—all experiences are meticulously designed, proprietary, and vertically integrated—rather than the Windows-style model of gathering developers to create third-party applications (which may create functional breadth but often lack security and a unified user experience). More broadly, this reflects the fundamental difference between closed and open architecture systems.
Performance and Finality
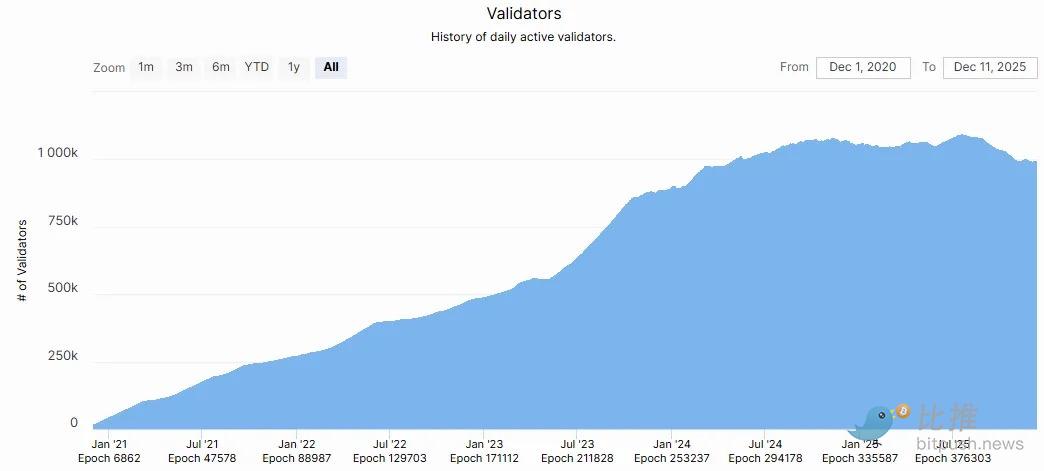
(Source: Ethereum Validator Distribution Chart)
Tempo is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Developers can use the same tools, languages, and frameworks (e.g., Solidity, Foundry, Hardhat) as on Ethereum to deploy and interact with smart contracts. Its consensus algorithm uses Simplex BFT consensus (originating from Commonware, to which Tempo has invested $25 million). The validator set is currently private and permissioned, an expected design for the initial stage of a private company.
In contrast, Ethereum is antifragile and anti-censorship, meaning anyone can freely join or leave the validator set. There are currently about 1 million daily active validators on the chain.
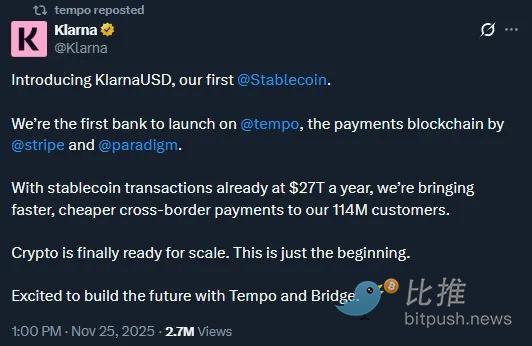
Overall, the core impression of Stripe/Tempo is: it is advancing rapidly with a vertically integrated product approach, aiming to capture the fintech market. Its partnerships with AI companies, Web2 enterprises, and traditional banks fully demonstrate its strength in driving blockchain commercialization.