Written by: Pengu, GCR
Compiled by: AididiaoJP, Foresight News
Original title: Why Blockchain is the Ultimate Answer to the Large-Scale Adoption of Humanoid Robots?
Introduction
Humanity has always pursued higher efficiency and greater productivity. From steam engines and electricity to assembly lines and computers, and now to artificial intelligence, each technological leap has brought about increased output and social prosperity, continuously reducing the resistance to value creation.
Past technological innovations have always relied on humans. Steam engines required workers to operate, factories needed a large labor force, and even every critical step of computing depended on people. These tools amplified human capabilities but never truly replaced human labor. While productivity improved, the role of humans remained irreplaceable.
Artificial intelligence has changed this. For the first time in history, software can build software on its own. Machines can autonomously complete the writing, testing, and optimization of code, meaning that intellectual labor is no longer the core bottleneck constraining growth.
Currently, this shift primarily affects white-collar work—programming, design, research, coordination, etc. Output in the digital world is growing rapidly, but physical production has not kept pace. Meanwhile, the demand for physical goods and services continues to rise, especially in areas like housing, food, logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare. The gap between digital productivity and physical output is becoming increasingly pronounced.
And robots are the key to bridging this gap.
Current State of Robotics Technology
Robots have long been used in industrial, medical, logistics, and aerospace fields. But the change today lies not only in their enhanced capabilities but also in their move beyond closed environments into human daily life spaces, including home settings.
The emphasis on "humanoid" stems from the fact that our physical world is designed for humans—doors, tools, stairs, warehouses, hospitals, etc. Rather than retrofitting infrastructure, it is more practical to develop robots that can directly integrate into existing environments. This also makes humanoid robots the shortest path from prototype to practical application.
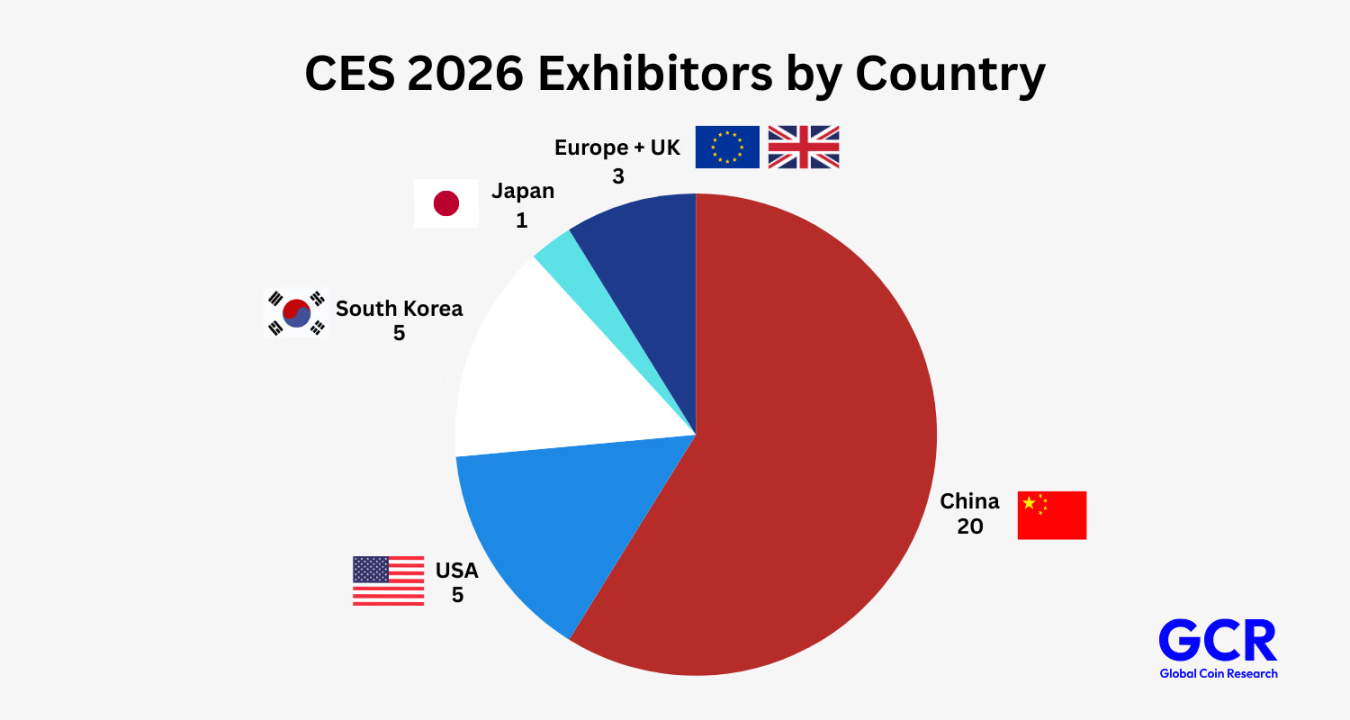
Humanoid robot technology is advancing exponentially, as evident at the 2026 International Consumer Electronics Show. What is remarkable is not just the more impressive demonstrations but the faster iteration speed in movement, manipulation, and autonomy. Progress has shifted from linear to exponential growth.
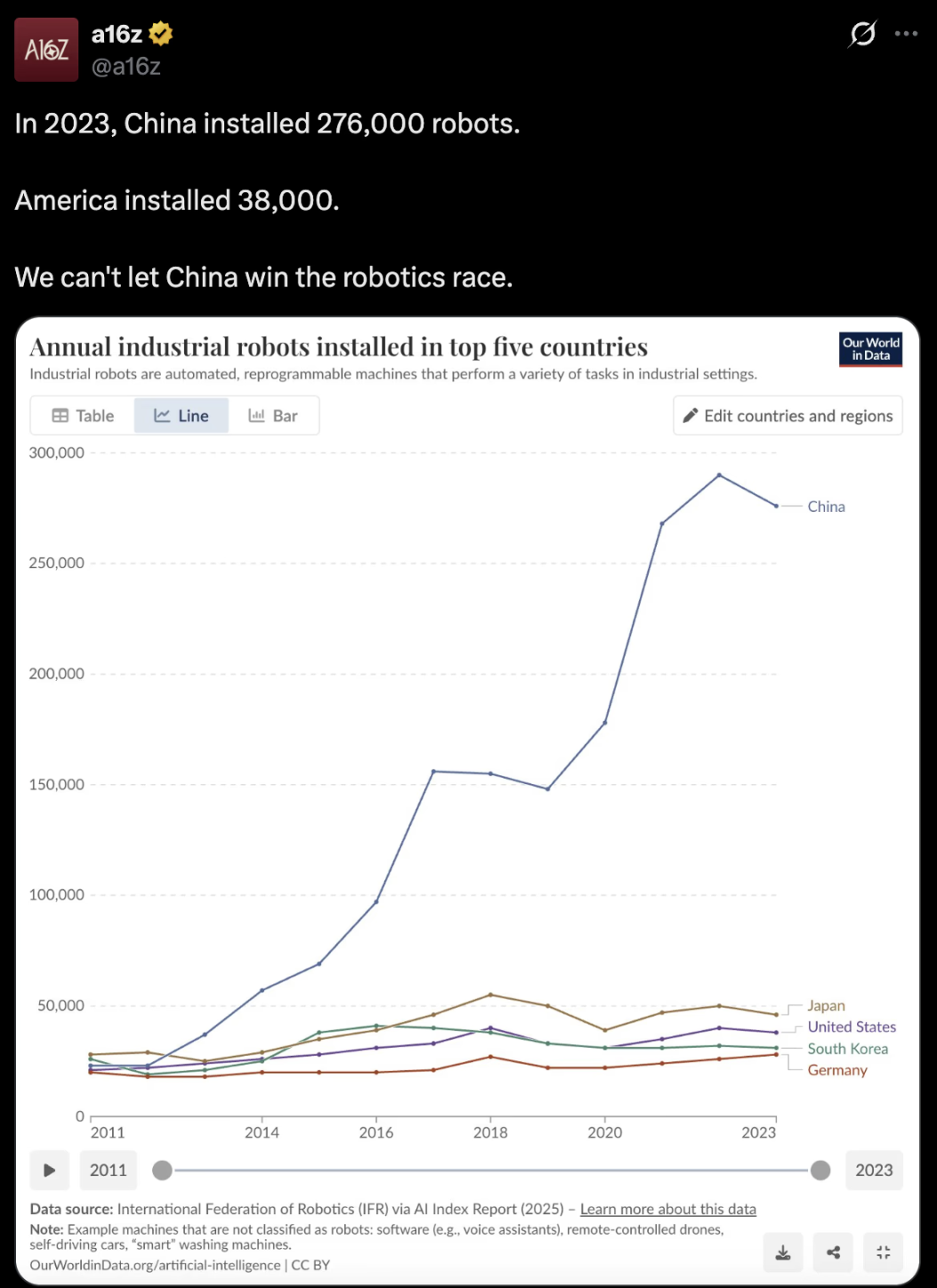
The integration of AI has completely transformed the development trajectory. Robots are beginning to learn from their own experiences, autonomously optimizing movements, balance, and task execution without the need for constant human supervision. As deployment scales up, data accumulates, and AI intelligence continues to improve, the feedback loop strengthens. The more robots there are, the faster the technological progress.
At the national level, robotics technology is also becoming a strategic priority. More and more governments view humanoid robots as core infrastructure related to productivity, resilience, and long-term economic strength. This is no longer just a commercial race but a contest for geopolitical influence.
According to Counterpoint Research data, approximately 16,000 humanoid robots were deployed globally in 2025, with China accounting for over 80% of the total. This highly concentrated distribution reflects China's proactive stance in promoting the adoption of humanoid robots. Adoption has shown clear regional differences and strategic drivers.
Looking ahead, Morgan Stanley predicts that by 2050, about 90% of humanoid robots (approximately 930 million units) will be used for repetitive, simple, and well-defined tasks, primarily in industrial and commercial sectors. China is expected to lead with about 302.3 million units, while the US is projected to have around 7.7 million.
The economic impact is already on the horizon. McKinsey & Company notes that if businesses can restructure workflows around "people, AI agents, and robots working together," rather than automating individual tasks in isolation, it could unlock up to $2.9 trillion in economic value in the US alone by 2030.
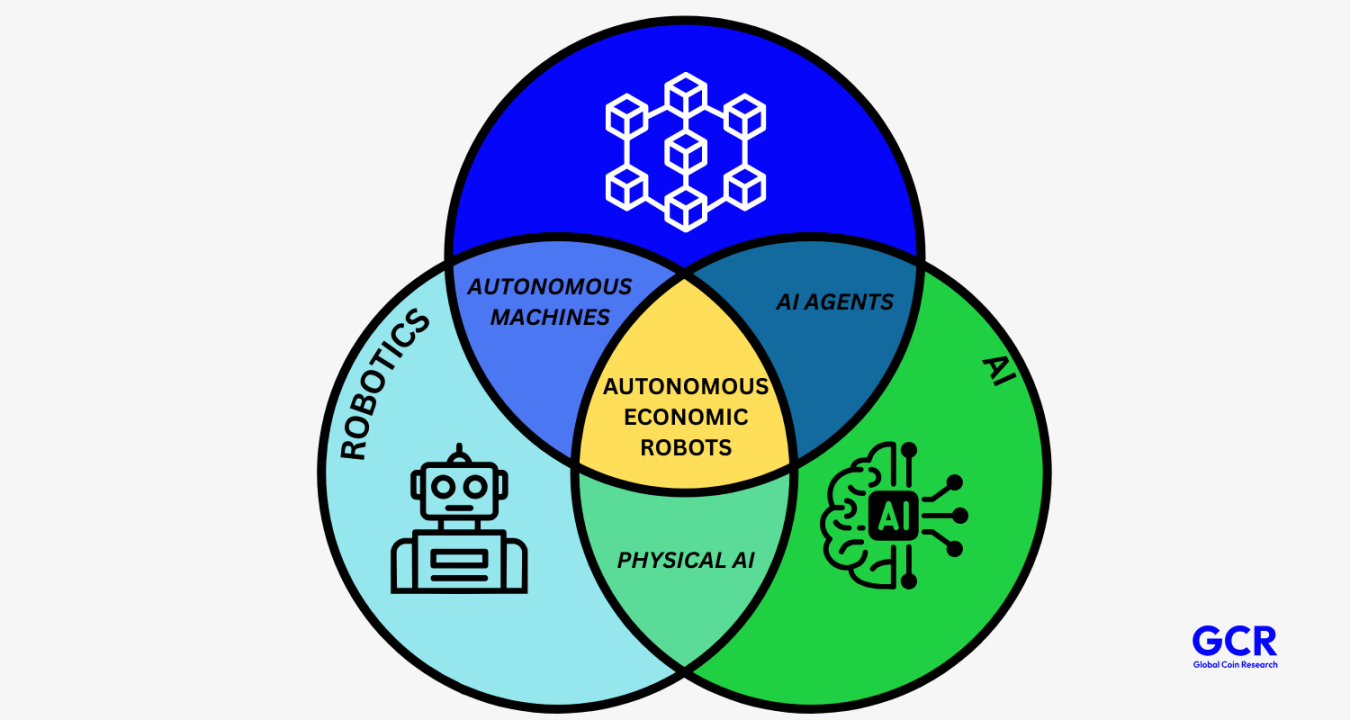
Robotics × Cryptocurrency
Currently, cryptocurrency is still primarily seen as a financial tool—trading, speculation, payments, and value storage dominate the narrative. But the potential of its underlying technology extends far beyond finance.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency introduce a new coordination layer for both the digital and physical worlds. As robots scale, the importance of this layer becomes increasingly evident. Robots will need to transact, own resources, share data, and operate across borders without relying on traditional financial and legal systems.
Cryptocurrency is the infrastructure that supports the scalable operation of robots.
Machine-to-Machine Payments
Robots operate continuously, with transaction frequencies far exceeding those of humans. Cryptocurrency enables instant micro-payments between machines, without bank intermediation, invoices, or settlement delays. This will be crucial once robots start autonomously purchasing services, energy, or tasks.
Robots as On-Chain Economic Agents
Robots are not just task executors; they will also become participants in economic activities. Being on-chain allows robots to directly receive payments, hold assets, and interact with smart contracts, transforming them from tools into autonomous economic agents.
Web3 Native Wallets Replace Traditional Bank Accounts
The traditional financial system is not designed for machines. Web3 wallets allow robots to open accounts instantly and globally without permission, significantly lowering the barrier to deployment and supporting cross-border operation from day one.
Tokenized Ownership of Robots and Clusters
Robotics is capital-intensive, and traditional financing is slow. Tokenization enables shared ownership of robot assets, revenue distribution, and liquidity provision, allowing investors to invest in robots as they would in digital infrastructure.
Blockchain-Based Machine Learning Data Distribution
Robots generate massive amounts of real-world data. Blockchain technology enables transparent ownership, controlled sharing, and value monetization of data. Better data access leads to more efficient training and more powerful machines.
Decentralization and Privacy Protection
As robots enter homes, hospitals, and workplaces, they will handle vast amounts of sensitive data—health records, behavioral data, physical environment information, etc. This should not be controlled by a single centralized entity. Decentralized systems reduce centralization risks and give users control over data access and usage. Cryptocurrency supports verifiable rules and privacy-preserving collaboration, which is crucial for building trust and driving adoption.
Projects Worth Watching
The robotics field has not received the attention it deserves. Current public focus remains on software and pure AI narratives, while physical automation quietly gains momentum.
As humanoid robots, AI, and crypto infrastructure begin to converge, the narrative is shifting. Below are some projects we are watching in this emerging field.
PrismaX — Driving Learning Through Teleoperation
PrismaX positions itself as a service layer for real-world AI robotics, converting human operation into high-quality training data through teleoperation to continuously optimize models and robot capabilities. Users remotely control robots to complete simple pick-and-place tasks, with each interaction becoming data for training autonomous systems. Human input serves as the bridge between current robots and full autonomy, making the learning process scalable and distributed rather than confined to labs.
Core Value
Robots excel in ideal controlled environments, but to the real world, they must encounter uncertainty, edge cases, and imperfect conditions. Rich and diverse datasets are essential for robots to work reliably in unknown environments.
Auki — Mapping for AI
Auki is building what can be called an "AI map" network. At its core is posemesh, a decentralized machine perception network that allows robots, smart glasses, and other devices to securely and privately share spatial data and computing power, enabling machines to form a shared understanding of the physical world.
By creating a "real-world web," Auki makes physical locations browsable, navigable, and searchable for AI systems. Robots and digital devices can coordinate in the same space without central control, while a token economy facilitates the exchange of spatial data and computing resources. The physical world thus becomes "machine-readable."
Core Value
About 70% of the global economy is still tied to physical locations and human labor. Enabling AI to understand and access the physical world is crucial for robotics, automation, and real-world applications to scale beyond digital environments.
GEODNET — Building a Positioning Network for an Autonomous Future
GEODNET is building a real-time kinematic positioning network that provides centimeter-level accuracy. The project has been listed by Grayscale as an asset under consideration for inclusion. It adopts a decentralized model where users earn crypto rewards by operating satellite reference stations while supporting real-world infrastructure. Participants not only gain passive income but also contribute to enabling large-scale high-precision navigation.
The network supports key applications such as AI robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and the metaverse, providing these systems with the essential spatial and temporal infrastructure.
Core Value
Centimeter-level positioning accuracy and nanosecond-level time synchronization are the cornerstones of autonomous systems. As robots operate increasingly independently in the physical world, reliable positioning becomes indispensable infrastructure.
Peaq — The Economic Layer for Robots
Peaq is the economic system and coordination layer for the machine economy. It is a blockchain optimized for machines, robots, and autonomous agents, offering native standards for identity, ownership, time, access control, and payments, enabling devices to participate in economic activities without human intermediaries.
On Peaq, users can own robots that work, generate income, and automatically distribute profits. Robots thus become productive assets rather than fixed costs, with coordination automated at the protocol layer.
Core Value
Robot scaling requires a native economic layer. Peaq provides the infrastructure to support ownership, incentives, and coordination for machines operating autonomously in the real world.
IoTeX — On-Chain Identity Layer
IoTeX is committed to building blockchain infrastructure that connects AI systems with the physical world. As AI moves beyond purely digital environments, its effectiveness increasingly depends on real-time, trustworthy real-world data. IoTeX addresses this through "Realms"—which aggregate real-time data from machines, sensors, and people to generate intelligent knowledge bases applicable to fields like mobility, health, energy, and robotics.
Another core component is ioID, an on-chain identity layer for machines and AI agents. Each ioID is paired with a globally unique identifier and an on-chain wallet, enabling discoverability, economic autonomy, and trusted interactions among machines, agents, and AI systems, making machines verifiable participants in the physical AI economy.
Core Value
Humanoid robots face complex tasks requiring mobility, perception, adaptability, and continuous learning. "Realms" provide continuously updated real-world data and domain intelligence, supporting robots and AI systems to operate reliably beyond controlled environments. Combined with ioID, robots become identifiable, trustworthy, and economically active primary participants in the physical AI economy.
Conclusion
Despite challenges in robot learning, mobility, environmental adaptability, cost, and legal frameworks, one trend is clear: robots will become an indispensable part of daily life. Homes, workplaces, logistics, healthcare, and cities will increasingly rely on autonomous machines.
For robots to achieve scale, intelligence and hardware alone are not enough. They also need identity, payment, coordination, and trust mechanisms that are recognized across borders and institutions. This is where cryptocurrency transitions from "optional" to "essential."
Robotics executes in the physical world; cryptocurrency coordinates in the economic world. Their convergence is shaping a new ecosystem that operates autonomously.
Twitter:https://twitter.com/BitpushNewsCN
Bitpush TG Discussion Group:https://t.me/BitPushCommunity
Bitpush TG Subscription: https://t.me/bitpush