1. Progress of the Fed's digital dollars
1.1 Detailed interpretation for the contents of recent digital dollar proposals
Due to the strong negative impact of the recent COVID-19 emergency on the US economy, Congress has proposed a series of proposals to recover from the emergency, which have mentioned digital dollars repeatedly.
1.1.1 The "Digital Dollar" draft of the House of Representatives
As early as March 22, U.S. time, Democratic Speaker of the U.S. House Pelosi mentioned digital dollars for the first time in her draft economic stimulus bill against COVID-19 "Take Responsibility for Workers and Families Act". Meanwhile, Representative Maxine Waters submitted the "Financial Protections and Assistance for America’s Consumers, States, Businesses, and Vulnerable Populations Act" (H.R.6321), which is part of the above-mentioned "Responsibility Act" and also contains digital dollar-related content, mainly appearing in "Direct stimulus payments for families". The above bill suggests the definition of digital dollars and the rules of digital dollar wallets as follows:
1) Definition of Digital dollar: (i) a balance expressed as a dollar value consisting of digital ledger entries that are recorded as liabilities in the accounts of any Federal reserve bank; or (ii) an electronic unit of value, redeemable by an eligible financial institution (as determined by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System).
2) Pass-through digital dollar wallet: A digital dollar wallet or account, maintained by a member bank(required) and other commercial banks or credit institutions subject to FDIC supervision(optional) on behalf of a qualified individual, where such qualified individual gets financial stimulus and chooses to set up a "pass-through digital dollar wallet".
(i) Separate: Each member bank shall establish and maintain a separate legal entity for the exclusive purpose of holding all assets and maintaining all liabilities associated with pass-through digital dollar wallets. The assets and liabilities of any legal entity shall not be deemed assets or liabilities of the member bank or its affiliates.
(ii) 100% deposit reserve: The assets of any entity shall consist exclusively of a balance maintained in a master account at a Federal reserve bank, and the liabilities or obligations of the entity shall consist exclusively of an equal quantity of balances maintained by holders of pass-through digital wallets.
(iii) Member banks with total consolidated assets in excess of $10,000,000,000 shall promptly offer individuals the ability to apply, through online or telephonic means, for a pass-through digital dollar wallets.
(iv) Member banks shall ensure that a pass-through digital dollar wallet established under this section: may not be subject to any account fees, minimum balances, or maximum balances; shall pay interest at a rate not below the greater of the rate of interest on required reserves and the rate of interest on excess reserves; shall provide functionality and service levels not less favorable than those that the member bank offers for its existing transaction accounts (including with respect to access to debit cards and Automated Teller Machines, online account access, automatic bill-pay and mobile banking services, customer service, and such other services as the Board determines), except that pass-through digital dollar wallet shall not include overdraft coverage; shall be prominently branded in all account statements, marketing materials, and other communications of the member bank as a ‘‘pass-through FedAccount’’ maintained by the member bank on behalf of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
(v) Protection: may not be closed or restricted by the member bank on the basis of profitability considerations; and shall provide holders with reasonable protection against losses caused by fraud or security breaches.
(vi) Cost reimbursement: Each member bank with total consolidated assets not greater than $10,000,000,000 shall be reimbursed each calendar quarter by the relevant Federal reserve bank for actual and reasonable operational costs incurred by the member bank in offering pass-through digital dollar wallets. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System shall issue rules to carry out subparagraph.
3) Digital dollar wallet: A digital wallet or account maintained by a Federal reserve bank on behalf of any person. The account requirements (iv) and protection (v) of the digital dollar wallet are the same as these of pass-through digital dollar wallet. Differences are as follows:
(i) Not later than January 1, 2021, all Federal reserve banks shall make digital dollar wallets available to all citizens and legal permanent residents of the United States and business entities for which the principal place of business is located in the United States.
(ii) In geographic areas where physical access to a branch of a Federal reserve bank is limited, Federal reserve banks serving such areas shall partner with United States Postal Service branch offices to ensure access and availability to application and account services for digital dollar wallets.
(iii) Shall provide, in conjunction with the United States Postal Service, access to automated teller machines to be maintained on behalf of the Board by the United States Postal Service at branch offices;
(iv) The “FedAccount” mark is required for digital dollar wallets and accounts.
4) Direct Stimulus Payments For Families: (i) first, by direct deposit (including to a pass-through digital dollar wallet), if the Commissioner has sufficient information to make direct deposit payments to the applicable individual; and (ii) otherwise, by check.
Unfortunately, on March 23, in the final version of " Take Responsibility for Workers and Families Act " (HR6379), the section on "Direct stimulus payments for families" was removed directly, so the proposal for digital dollars was not included in this economic stimulus proposal. However, the final proposal of the House of Representatives is still in the "proposed" state and has not yet entered the voting link. On March 27, the Senate ’s $2 trillion economic stimulus bill(H.R.748) has been signed by Trump and officially became law.
1.1.2 Senate's "Digital Dollar" draft
On March 23, when the House of Representatives submitted the final draft version, Senator Sherrod Brown also put forward a proposal on Digital Dollars "A Bill to require member banks to maintain pass-through digital dollar wallets for certain persons, and for other purposes" (S.3571) , which is a special proposal for digital dollar wallets, with more independent and not only applied to economic stimulus in COVID-19 situations.
Senator Sherrod Brown ’s proposal is basically the same as the digital dollar part of the House draft. There are some differences in the following details:
(i) Definition of digital dollars: directly in the form of liabilities, there is no definition of institutional redemption.
(ii) Strengthening the description of inclusive finance: In areas where access to physical member bank branches is limited, including in low- or moderate-income geographies, designated disaster areas, distressed or underserved non-metropolitan middle-income geographies, as designated by the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council, Federal reserve banks shall partner with postal retail facilities to ensure access and availability to application and account services for all residents and citizens of the United States and to businesses domiciled in the United States.
(iii) Adding privacy provisions: Section 552a of title 5, United States Code (commonly known as the "Privacy Act of 1974"), shall apply to digital dollar wallets, and the privacy obligations applicable to each Federal reserve bank and its employees.
At present, the final version of the bill has not been uploaded to the official website of Congress, while the progress of the proposal is still "proposed".
1.1.3 Summary of the main points of the two proposals
From the proposals of the House of Representatives and the Senate, we can see the design ideas of digital dollars by some American government officials:
1) Central bank currency of 100% reserve: digital dollar is defined as the central bank ’s liabilities or central bank redemption, which has the same value support as that of the US dollar. Although the “pass-through digital dollar wallet” is established and maintained by commercial banks or other financial institutions, these banks need to establish a master account with a 100% deposit reserve in the central bank. Therefore, there is no deposit currency expansion at the level of commercial banks, and all digital dollars are directly the central bank currency.
2) Both the first- and second-layer operating structure: digital dollars are issued and paid through digital wallets. The Federal Reserve Bank directly opens "digital dollar wallets" (the first layer), Federal Reserve member banks and other commercial banks regulated by FDIC establish "Pass-through digital dollar wallet "(the second layer), the function and interest of the wallet are the same as bank account.
3) Promoting inclusive finance: digital dollar wallets need to ensure access to all individuals and businesses, and the threshold for wallet accounts is further reduced without account fees and balances limits. Direct digital dollar accounts of the Federal Reserve Bank can also use funds through ATM .
From the perspective of the BIS currency classification, the digital dollar plan in the proposal is actually a type of central bank settlement account (retail), which meets the central bank's issuance, digital form, availability for everyone (non-wholesale) and account-based systems. Since the proposal does not specify whether it is based on distributed ledger technologies such as blockchain or whether it replaces cash, it is impossible to determine whether the digital dollar may be based on Token.
The design of the digital dollar corresponds to the demand of the US government for economic stimulus under the COVID-19. Digital dollars can directly pass government financial subsidies and central bank's monetary policy to various users through wallets accurately and without contact.
1.2 Changes of the Fed's attitude towards digital dollars
Before many proposals involving "digital dollars", in fact, the US attitude towards the central bank's digital currency has been relatively dull, and the progress of research and discussion has been relatively slow.
In the second half of 2019, due to the launch of Libra, the governments of various countries reacted violently, and the central banks began to study, design, and test the central bank's digital currency to speed up its CBDC process. The United States responded calmly during this period. In November 2019, Fed Chairman Powell responded to MPs ’inquiries on September 30 this year about the Federal Reserve ’s Development of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC): " So far, the Fed has not been clear about the implementation of monetary policy and the obvious benefits of general (retail) CBDC compared to existing tools. "" The U.S. payment field is currently highly innovative and competitive, and consumers have many fast and reliable digital options. It is unclear what new value CBDC may bring to the U.S. ", which suggested that the Fed believes that the United States may not currently need to issue digital dollars. In December, at the House Financial Services Committee hearing, US Treasury Secretary Mnuchin also said that Powell and he agreed that in the next five years, The Fed does not need to issue digital currency.
After 2020, the attitude of the US government and the central bank began to undergo some changes, recognized the central bank's digital currency research. In a speech at the Stanford Business School on February 6th, Federal Reserve Board member Lael Brainard stated that the Federal Reserve is "undertaking research and experiments related to distributed ledger technology and its potential use cases for digital currencies, including the potential of CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency)". "We hope that by changing the payment method, digital currency can obtain greater value at a lower cost and provide more convenience to the people." She added that the global importance of the US dollar means that the Fed needs to "maintain the forefront of research and policy making" in terms of digital currencies. On February 11th, Powell proposed at the House Financial Services Committee that Libra and China's DCEP have indeed aroused great concern, and the Fed has also studied this. But he pointed out that "China and the United States have different systems, and a book that can understand the payment behavior of all citizens may not be attractive in the United States." This attitude suggests that the US central bank's digital currency may support a more privacy-oriented approach. On February 14, Fed Commissioner Judy Shelton stated that the digitization of the US dollar will help maintain the US dollar ’s dominant position in global trade: "Competing countries are working hard to find alternatives to the US dollar. We must be ahead of the times to ensure that the US dollar continues to be the best currency of the world, which is very important. "
1.3 The summary of the progress of the Fed's digital dollar and the comparison of CBDCs in various countries
In summary, the Fed is currently in the stage of researching well-known digital currency projects and central bank digital currencies, and there is no very definite deployment plan. From the limited speech and deleted proposals, it can be speculated that if the Fed issues digital dollars, the main strategies and factors it will consider are: 1) always need to maintain the international dominance of the dollar; 2) can enhance the convenience of payment, especially in the emergency moments such as the COVID-19, using its high efficiency and non-contact features to better maintain economic stability and conduct monetary and fiscal policies; 3) ensure user privacy; 4) improve inclusive finance.
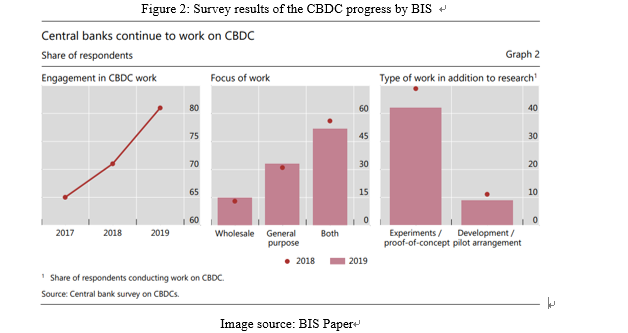
At present, dozens of countries have begun central bank digital currency research and testing. BIS conducted a new central bank digital currency survey at the end of 2019, surveying 66 countries, including 21 developed countries and 45 emerging countries, covering 90% of the global economic productivity of 75% of the population around the world. Among them, 80% of countries began to work on central bank digital currency, which was 70% at the end of 2018. 40% of countries have progressed from the research stage of CBDC to the stage of experiment and proof of concept, and 10% of the countries (both emerging countries) have entered the pilot stage.
2. Development of U.S. non-governmental digital currency
2.1 Well-known non-governmental digital currency
Although the official Fed digital currency is not yet clear, a large number of U.S. companies have issued or plan to issue U.S. dollar digital currency, or U.S. dollar Stablecoins, that is, 100% reserve, anchoring the U.S. digital currency.
In 2018, several US trust institutions and enterprises holding MTL and BitLicense licenses issued compliant Stablecoins USDC, TUSD, GUSD, and PAX, which are widely used by cryptocurrency exchanges and blockchain applications around the world. In February 2019, JPMorgan Chase issued a 1: 1 dollar-pegged Stablecoins JPMCoin, and the US dollar reserve was placed in a designated account of JPMorgan Chase. JPMCoin is mainly used for the flow of funds between JPMorgan Chase ’s national Subsidiaries, as well as JPMorgan and its business partners. JPMorgan Chase ’s business is spread all over the world, and more companies have business partnerships with it. By using JPMCoin, it has strengthened the flow of US dollars among global banking institutions. In March, IBM launched the payment network WorldWire, which is based on Stellar and can realize efficient cross-border payment between banks and institutions. Previously, it has issued a stable dollar USD “Stronghold USD” in cooperation with San Francisco startup Stronghold. At present, IBM has signed letters of intent with six banks around the world. IBM also said that the World Wire network covers 72 countries, 47 currencies and 44 kinds of "bank terminals" (including banks and ATMs). In June 2019, Facebook launched the Libra Association, planning to issue a Stablecoins Libra that anchors a basket of currencies. Thanks to Facebook's 2.7 billion users, Libra caused a stir in the world. At present, 50% of Facebook's basket of reserves is the US dollar, which occupies a dominant position and can magnify the international status of the US dollar. Recently, it has been rumored that Libra may change the design route to issue its payment network firstly to play the role of inclusive finance. With regard to currency reserves, there are also many rumors that the possibility of changing to a single dollar-pegged currency cannot be ruled out. In March 2020, the US dollar Stablecoins Celo announced plans to launch in April, containing some of the Libra Association participants. Compared to Libra, Celo anchors the US dollar only, so its compliance process is smoother. Both are committed to promote inclusive finance. Celo's leader Chuck Kimpo said the new currency will be issued in the United States, but the alliance's future issuance will focus on Latin America, Africa and Southeast Asia.
In addition, there are a large number of non-profit institutions and associations in the United States actively conducting research and assumptions on digital dollars. The former US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) chairman recently participated in the establishment of the Digital Dollar Foundation together with Accenture(https://www.digitaldollarproject.org/), which is the most representative. The project has currently joined 22 consultants to promote the exploration of the Central Bank of America's digital currency (CBDC), to encourage research and open discussion on the potential advantages of digital dollars, to convene private sector thought leaders and actors, and to propose the possible models supporting the public sector, it is reported that a white paper will be released within two months. The project will establish a framework for potential practical steps to establish USD CBDC. The project mentioned that the digital dollars issued by the Federal Reserve should expand the scope, diversify and elastic of dollar acquisition and payment, and support retail, wholesale and international payment cases: 1) Online retail payment: digital dollars will provide new options, instant peer-to-peer payment, and a variety of payment methods for digital transactions, especially in the case of intensified financial crisis, giving greater autonomy. Digital dollars can be distributed to end users through commercial banks and trusted payment intermediaries which provides other mechanisms to ensure and promote inclusive finance. 2) Wholesale payment: Provide more diversified access methods for large payments and support the establishment of digital financial market infrastructure. 3) Cross-border payments: Traditional international payments cannot be digitalized in US dollars. Digital dollars will allow for more direct currency relationships. With digital payments in central bank currency, offshore securities settlement reduces risks, the continuing shortcomings of the existing agency model have been resolved, the competitiveness of international payments has improved, and financial market integration has been promoted. The Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE), one of the two major think tanks in the United States, also released a research report on digital dollars in March, proposing a regulated digital dollar account system for consumers, which is managed and fully supported by the Federal Reserve, similar to Alipay based on distributed ledger technology. It can be seen that the US private sector's demand for the creation of USD CBDC is relatively urgent and strong.
2.2 The role and impact of non-governmental digital stablecoins
2.2.1 Auxiliary tool to help the central bank's digital currency continue its dollar status
At present, the US dollar is the dominant currency in the global economic and financial markets. The key elements to measure its influence are the settlement ratio, pricing ratio, and reserve ratio of the US dollar in the international market. Therefore, to improve the currency's influence and international status, the key is to increase its widespread use and storage worldwide. Non-governmental digital currency can be used as an auxiliary tool to help the US dollar to promote globally and continue its international status.
First of all, many companies that currently issue USD stablecoins are large multinational corporations with global networks and user advantages. Like Libra, Facebook has 2.7 billion users worldwide and is the best tool to penetrate retail users; JPMorgan Chase is one of the world's leading financial groups and the largest financial services institution in the United States, with more than 5,100 commercial banks in 2017; IBM is also one of the leading multinational technology companies, with more than 380,000 employees worldwide and countless corporate customers.
These companies with extensive network advantages can use existing customers as a resource to promote the US dollar, allowing the digital stablecoins that anchors the US dollar to penetrate into the global customer network, such as JPMCoin stipulates between many molecular companies of JP Morgan Chase and other commercial banks for clearing and settlement, Libra can pay directly in Facebook software, so it can increase the use of US dollars and further consolidate the international status of the US dollar. Moreover, in some non-developed countries that have not yet reached the US dollar, they can be reached through a network of multinational companies, while using the credit and stability advantages of the US dollar to accelerate penetration into countries with weaker monetary systems in the name of inclusive finance. This is why when the central bank governments of many countries question Libra, the attitude of the US government is more positive and inclusive.
On the other hand, the blockchain-based transfer system is recognized as efficient and convenient in the field of cross-border payment. The current global payment communication network Swift is a tool used by the United States to control the lifeline of global payments, but it has also been criticized for its inefficiency problems. In recent years, various cross-border payment networks based on blockchain have emerged in an endless stream. Therefore, the digital currency and blockchain system of American companies can be a test field for the central bank and the government to a certain extent. If they can develop and build an efficient and secure blockchain payment system, then they can also guarantee that the United States can rely on the advantages of this new payment to manage and master the global payment dynamics, continue the advantages of the global financial infrastructure established by the United States through Swift, and ensure the dominance of the US dollar.
But at the same time, we must also see that in terms of practical application and promotion, the popularization effect of non-governmental digital currency is inevitably far inferior to CBDC, which depends largely on the company's own influence and the functional design of digital currency. The more people it covers , The greater the response. For example, in 2018, the United States has issued a lot of compliant stablecoins, but the use of the currency is still in digital asset transactions. Due to network effects, the current number of users is not as good as the early issued USDT. The other hand is the design and use of digital assets. Since the wholesale digital currency is B2B, although its risk is less, the amount of attention and user reach are inevitably far less than retail digital currency. For CBDC, it can be directly promoted by the government, so the effects in all aspects will be significantly stronger.
2.2.2 Better versatility, lower political meaning
In the future, when the central bank's digital currency wants to take advantage of its cross-border payment, a very important consideration is compatibility and interoperability. Because most central banks, especially developed country central banks, will develop their own CBDC systems. If the systems between the central banks cannot communicate with each other, they cannot play their role. At present, BIS has formed the CBDC research groups of six central banks in January 2020. The central banks of Thailand, Hong Kong, Singapore and Canada have also conducted cross-border payment experiments based on blockchain. In the future, interoperability will require central banks of all countries to directly and actively cooperate.
Compared with the cooperation requirements of the central bank's digital currency, the digital stablecoins system issued by the enterprise will have better versatility and compatibility, and it can be globally promoted based on the enterprise's own global network and resources without the cooperation between governments. The cost of this experiment is also lower. At the same time, with the non-governmental digital currency as the facade, the political meaning is also relatively weakened, especially in the field of inclusive finance.
2.2.3 The risks of financial stability and security
In addition, the digital currency issued by the private sector may have higher financial stability and security risks than the central bank digital currency. This is also one of the reasons why many central banks consider issuing CBDC. Usually, CBDC has to go through a longer period of research and testing, and it needs to ensure sufficient safety and stability.
Generally speaking, the concern about non-government digital currency is that 1) it may affect the traditional financial industry, such as reducing bank deposits, causing run-off risks; 2) it may replace the central bank ’s currency and affect monetary policy; 3) money laundering, terrorist financing and other illegal events; 4) User privacy.
For the United States, first of all, the probability that the digital stablecoins issued by the private sector will affect the financial industry or the central bank ’s currency cash in the United States is small, because the US dollar stablecoins is not much different from the US dollar in domestic experience. From a historical perspective, the US dollar stablecoins has not become popular in the United States, and it is used more abroad.
Secondly, for money laundering and terrorist financing, there are currently corresponding compliance programs and plans. In terms of fund custody, the US dollar stablecoins USDC, TUSD, GUSD and PAX are issued or escrowed by companies with MTL or trust licenses. For payment, the United States has related licenses including MSB, MTL, Bitlicence, etc.
Finally, in terms of privacy, this is a long-term problem that needs improvement. It is only a problem of digital stablecoins, traditional bank accounts and corporate accounts all have privacy issues. In this regard, an appropriate regulation and framework is needed.
3. Analysis of changes of the Fed's attitude towards the digital dollar
We can analyze the main reasons why the central bank chose to issue CBDC to see the reasons for the changes in US attitude. The CBDC survey report of BIS shows the main needs of developed countries and emerging countries for CBDC related work, including financial stability, monetary policy implementation, inclusive finance, payment efficiency (domestic and cross-border), payment security, robustness, etc.
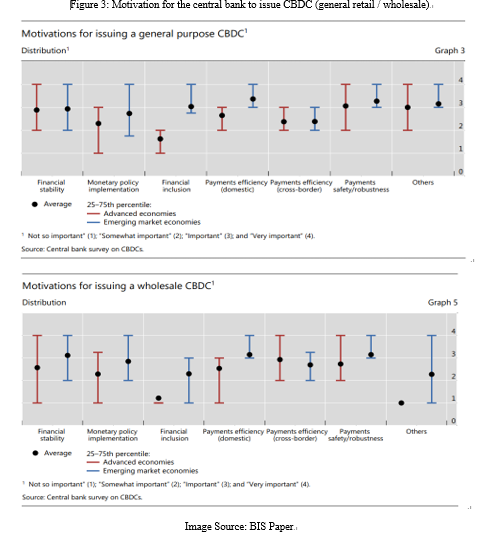
Combined with the BIS survey report and comprehensive analysis, it can be concluded that the main functions of CBDC include:
1) Domestic payment settlement: CBDC can realize digital payment, but this role is mainly aimed at developing countries with underdeveloped digital information infrastructure, which still uses a lot of cash, and can use CBDC to realize mobile payment and digitalization at one time. The demand in developed countries is relatively weak.
2) Cross-border payment and settlement: This is the most important role of digital currency. Both developed and emerging countries have strong motivations. Among them, wholesale CBDC has a stronger demand for this.
3) Inclusive finance: As the threshold for digital accounts is lower and not subject to geographical restrictions, inclusive finance is generally more powerful. This demand comes mainly from developing countries, or at special moments such as the COVID-19, mainly retail CBDC.
4) Financial supervision: Because the traditional central bank currency, namely cash, is anonymous, it is not conducive to supervision and control of illegal facts. By using CBDC instead of cash, better traceability and supervision can be achieved.
5) Strengthening the efficiency of currency control: Many countries currently face problems such as reduced cash usage. For example, Sweden's cash utilization rate is only 19%, the United Kingdom predicts that cash payments will account for only 9% of all payment methods by 2028. Cash is the currency of the central bank, which is issued and controlled by the central bank. It is not a deposit currency. If there is no cash, it means that the central bank's monetary policy means are reduced, especially the lack of direct channels for individuals. Therefore, by using CBDC instead of cash, with its traceability and peer-to-peer characteristics, it can play a precise currency placement and management function, and better realize monetary and fiscal policies.
6) Financial stability: Due to the continuous rise of various digital currencies, private digital currencies or CBDC in other countries may affect the national currency. Therefore, CBDC needs to be issued to deal with these potential threat risks.
7) Enhancing the international use and influence of currency: Blockchain-based CBDC can make faster and more efficient payments, which will enhance the attractiveness of currency, thereby promoting its more use for payment and settlement, and improving the use of currency and international influence force.
The Fed's attitude change mainly began in 2020, and in December 2019 it was still the attitude that "the CBDC will not be released within five years." Therefore, it can be judged that the most important reason for the Fed's attitude change is the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19, which has led to a significant increase in the Fed's demand for digital dollars. First of all, due to the intensification of the epidemic, the traditional contact payment methods such as cash and checks became invalid. At present, the proportion of cash payments in the United States is still relatively high. The Fed's 2018 report pointed out that cash payments account for 30% of all transactions, this proportion will increase significantly for small transactions. Therefore, there is a need for efficient and non-contact payment methods to meet the payment during the epidemic, and the motivation for domestic payment settlement has become obvious. In addition, because cash is unavailable during special periods, some people who do not have bank accounts, credit cards, etc. cannot use online payments, making it almost impossible to pay effectively during the COVID-19. According to statistics, 85 million people in the United States still have no access to sound financial services. The digital dollar account can be set up for US citizens in the form of a lower threshold, helping these people who do not have a bank account to effectively make payments and promote inclusive finance.
At the same time, in order to stimulate the economic recovery, the US government will need to increase the supply of money to regulate the economy and improve liquidity through monetary and fiscal policies. The people mentioned above who do not have sound financial services, usually those in difficult areas in less developed areas, need the most financial assistance. Traditional methods such as checks will be used with caution during the epidemic, and digital wallets, especially those directly under the Federal Reserve, can cover all citizens, and can meet the requirements of traceability and non-contact, more accurately implement central bank policies and become an effective money delivery tool in times of epidemic. Therefore, the role of the digital dollar in strengthening the efficiency of currency control will increase.
On the other hand, before the COVID-19, in fact, the introduction of Libra and various similar digital currencies and the introduction of CBDC in various countries have also paved the way and promoted the change of attitudes of the United States, especially the announcement and progress of China's DCEP. Taking the launch of Libra as a starting point, the European Union, France, Turkey, and the Bahamas have recently announced the start of central bank digital related projects and pilot projects. China, Sweden, Thailand and other countries have made significant progress in CBDC. A more positive attitude appeared in Switzerland, Japan, South Korea, etc., and they began to research and explore CBDC. Fed Chairman Powell emphasized in the House Financial Services Committee meeting on February 11 that Libra and China ’s DCEP have indeed aroused great concern, and the Fed has also studied this. These private digital currencies and other central bank digital currencies have actually brought a stronger trend of currency wars, which is a potential impact on the original global dominant currency of the US dollar. Therefore, it has also increased the demand for US to research on CBDC, with a view to consolidating its own position. The digital dollar design scheme proposed in PIIE ’s March report also confirmed the above points, namely the provision of cheaper and safer payment systems, maintaining the stability of the financial system, the provision of inclusive finance, and the provision of powerful and stable new policy tools for monetary and fiscal policies (accurate quantitative easing directly to consumers).
In general, the change in US attitude towards CBDC is due to: The launch of Libra and CBDC in various countries has strengthened global competition and played a bedding role, and the COVID-19 has acted as a fuse, significantly increasing the demand for digital dollars, and promoting the United States to become relatively recognized for the role of CBDC.
But overall, CBDC is a very complicated systematic project. The infrastructure of a developed country is relatively complete, and the corresponding transformation requires sufficient time and testing. The United Kingdom has been actively researching since 2016, and there is still no obvious progress. It is also impossible for the United States to achieve the impact of the epidemic, and it is more likely to be a slow transition. However, this progress of the United States is still a very positive signal. In the future, if the epidemic continues for a long time, the demand for precision currency delivery in the United States will be strengthened, and contact with paper will be more careful, which will increase the possibility of new progress.