Editor's Note: Will quantum computing become Bitcoin's "next existential test"? The community is not short of researchers and technical solutions on this issue, but those who truly determine the direction of the protocol are always that small group of core developers with substantial influence.
This article systematically reviews the public stances of Bitcoin's main developers on quantum risks and finds that: at the top decision-making level, quantum threats are still widely regarded as distant, theoretical problems rather than engineering challenges requiring immediate action. The continuous efforts of a few researchers have not yet translated into consensus or action, nor have they been able to shift the inertia of the core governance structure.
Below is the original text:
Recently, some Bitcoin developers have begun to refute the view that I and others have put forward, namely that Bitcoin developers are not concerned about the risks posed by quantum computing.
It should be obvious to anyone who has seriously followed the discussions that, when weighted by influence, the majority of Bitcoin developers either provide very long timelines or outright deny this threat. However, let's specifically examine Matt's statement.
I already knew the situation was like this, as I have been following these discussions, but after doing this review, I was still surprised by the depth of indifference shown by the most important developers.
A brief note on methodology: If you are unaware, who exactly the "levers of power" in Bitcoin development lie with is deliberately kept opaque. When Craig Wright legally harassed Bitcoin developers, some chose to "step back" or "retire," but in reality, they still contribute code to avoid his legal maneuvers. The list of Core Maintainers, those who actually push updates into Bitcoin Core, is not a list of "the most important Bitcoin figures," but rather people trusted to perform a bureaucratic task. Since Gavin Andresen, these individuals have deliberately distanced themselves from responsibility and ownership of Bitcoin. They repeatedly emphasize that they do not "control" Bitcoin, but that everything is decided by a vague stakeholder consensus. They often claim, in a nearly Rousseau-esque vague manner, to represent the "will of the people."
Of course, they don't actually ask global Bitcoin users if they agree with a certain change. The way it works in reality is: if you can convince about five or six of the most influential developers that a change is important, then that change might be pushed through. This is extremely difficult and very rare, so the result is—changes almost never happen. In the past decade, Bitcoin has only undergone two updates. And because of this structure, almost any change requires agreement from all "deemed important people." As one might imagine, this leads to deadlock and inaction. So far, this state has managed to barely function; but when Bitcoin begins to face an uncertain yet rapidly approaching threat that requires fairly drastic adjustments, this is precisely the worst possible governance structure. In the modern sense, Bitcoin has never truly faced an existential crisis; the last time there was a substantive survival issue (in 2010 and 2013), the governance structure was still centralized enough to quickly roll out fixes.
Therefore, although doing this is nearly "heretical" in the Bitcoin context and will certainly annoy developers, because it reveals the reality of their deliberately maintained "structureless" governance, I intend to try to determine: which developers have the greatest "perceived authority."
(A note on my background: I have studied Bitcoin professionally for ten years; my master's thesis was on Bitcoin governance; I have provided funding to Bitcoin development organizations through Castle Island; I have spoken at multiple Bitcoin conferences; and I have met and spoken with many of the developers mentioned here. No one can truly fully map the power dynamics of Bitcoin governance, but I am closer to this reality than most people.)
I am aware that ranking Bitcoin developers by "influence" will make many people uncomfortable, but for this analysis, this step is unavoidable. We must know who the real gatekeepers are to assess: are the most important Bitcoin developers really prioritizing quantum risk? You can certainly question my ranking or propose another standard, but the only thing that matters is—have I accurately identified those core threshold figures.
The reason this is so difficult is precisely because Bitcoin developers deliberately keep the power structure opaque to the public. I have followed this issue for a long time and have a relatively clear judgment of "who is truly important," but even so, this remains an extremely difficult task. And there's only one reason for this: the developers want it to remain difficult to see.
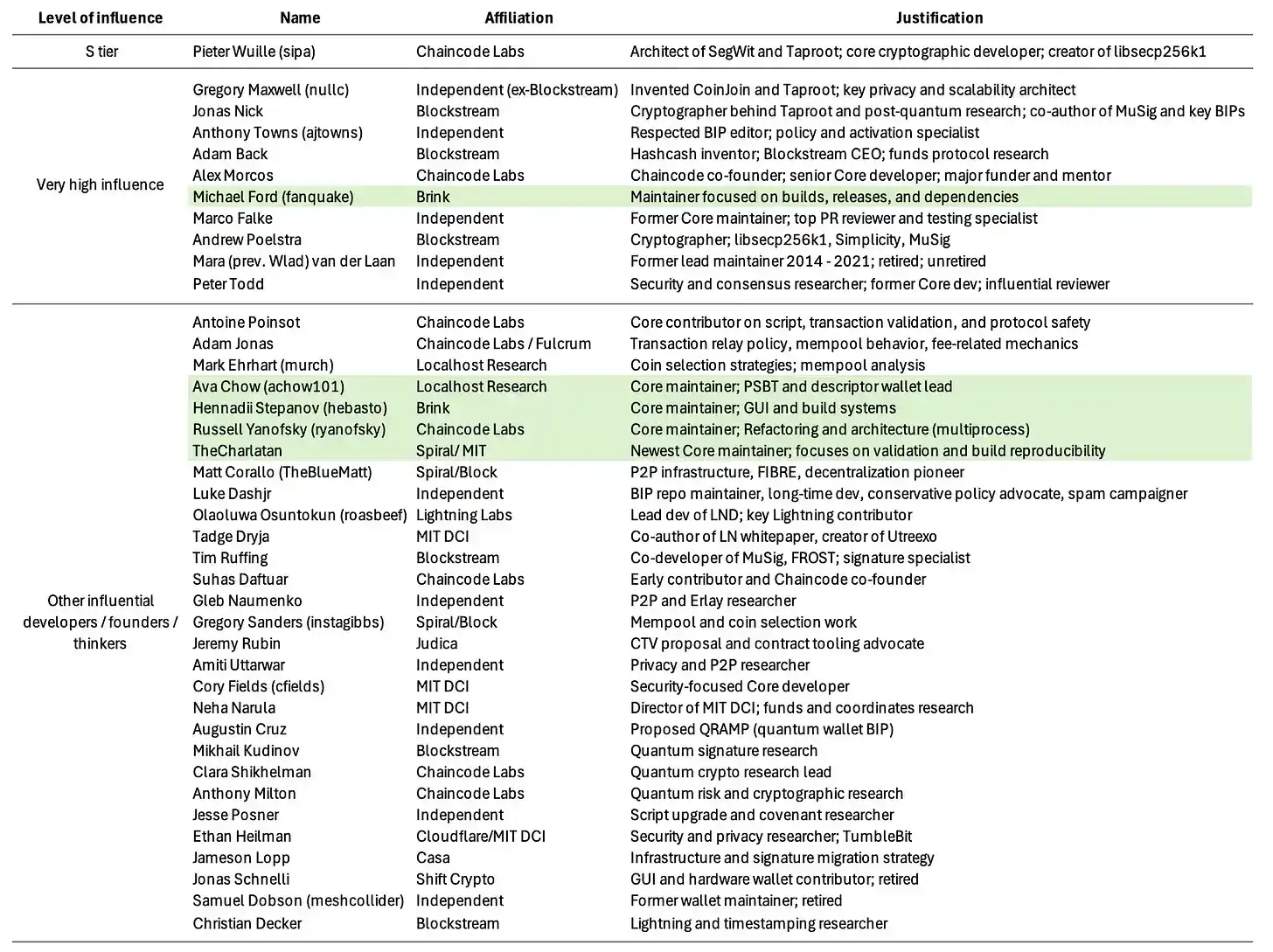
Those marked in green are Maintainers. The list is not complete and may contain errors. The influence ranking is my subjective judgment.
In my view, the most important Bitcoin developers/founders include: Pieter Wuille (undoubtedly in first place), Greg Maxwell, Jonas Nick, Anthony Towns, Adam Back, Alex Morcos, Marco Falke, Andrew Poelstra, Mara van der Laan, and Peter Todd. Their affiliated organizations are listed in the table.
Pieter Wuille is the co-author of SegWit and the main author of Taproot—the only two major upgrades to Bitcoin in the past decade. He created libsecp256k1, wrote the Schnorr signature specification, and co-proposed BIP9. In terms of driving major technical changes, he is by far the most important Bitcoin developer, bar none.
Mara van der Laan (formerly known as Wlad) served as the lead maintainer of Bitcoin Core from 2014–2021, officially "retired" in 2023, but has clearly returned in some significant capacity.
Michael Ford is one of the longest-serving current Core maintainers. While he doesn't directly write BIPs, his influence should not be overlooked.
Andrew Poelstra is the most low-key of all the "high-influence" developers, but his impact is enormous—you could say he is the "developer's developer," somewhat like Steely Dan. He is a co-author of the Taproot and Schnorr implementations and has made numerous important contributions across the field of cryptography.
Morcos runs an important developer organization, Chaincode. Michael Ford is currently the most prolific Core maintainer. Greg Maxwell is a legendary and opinionated developer. Adam Back was cited in the Bitcoin whitepaper, is the co-inventor of Hashcash, and is also the head of Blockstream.
Marco Falke was an extremely active reviewer in Core, although he stepped down from the key maintainer role in 2023. Jonas Nick is one of the main authors of Taproot. Peter Todd is a long-time active and widely involved Bitcoin developer, inventor of important mechanisms like RBF, known for his adversarial thinking and for blocking unsafe changes.
I would have included Luke Dashjr as well, but his recent influence has declined.
Every person mentioned here possesses a considerable degree of "soft power." Together, they decide whether an update will be taken seriously and ultimately implemented. If you cannot get almost everyone on this list to agree that your update is "important," it is almost impossible for it to happen. What we often call the "High Priests of Bitcoin" refers precisely to these people.1
The other developers and thinkers in the lower half of the list are certainly also important—after all, it's only a few dozen people collectively guarding a trillion-dollar asset, and I mean no disrespect to their contributions—but in my view, they are not the gatekeepers. Nevertheless, their opinions still carry significant weight, so I have listed them here as well.
How the Most Important Bitcoin Developers View Quantum Risk
Let's start with the "High Priests."
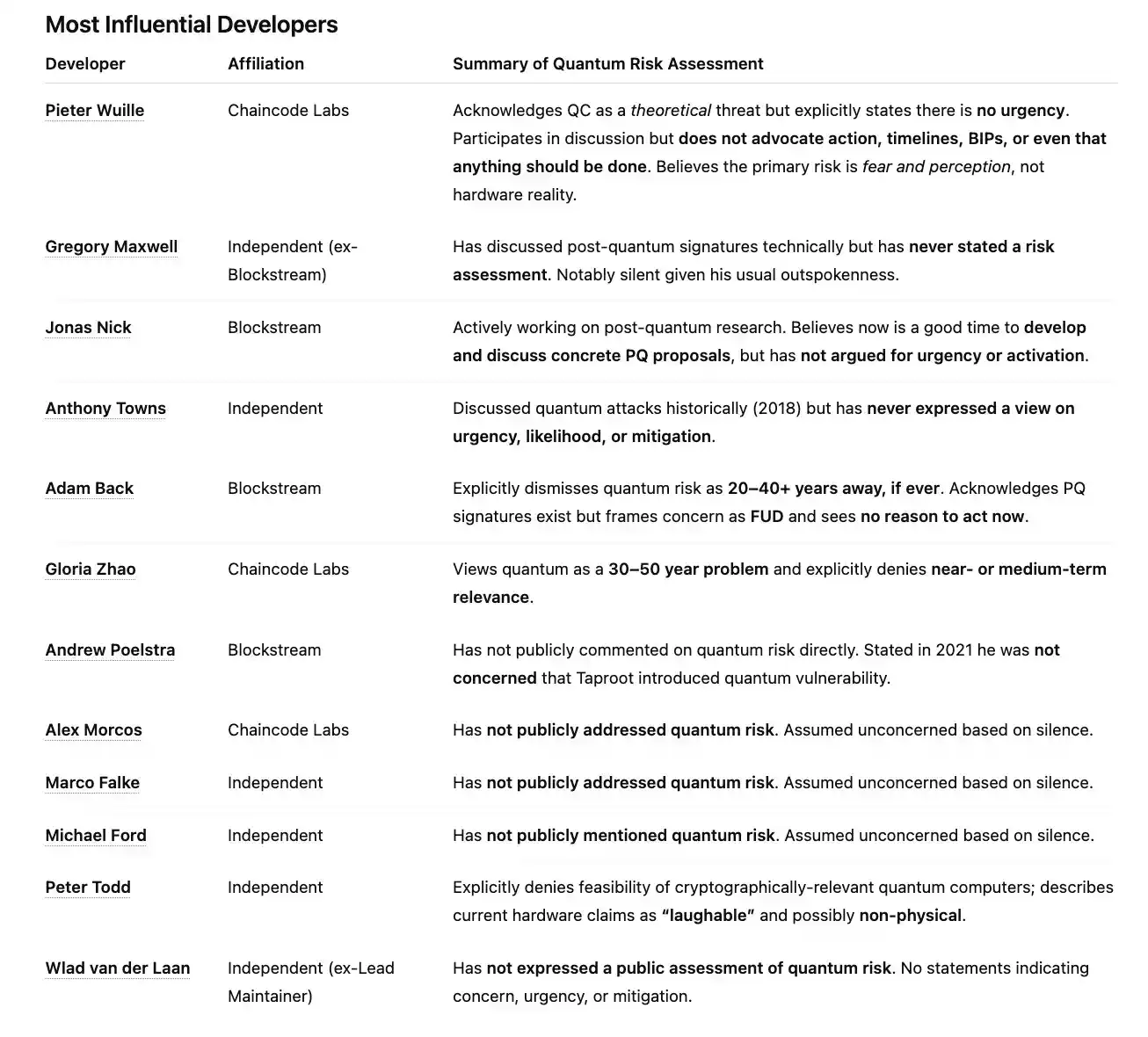
Pieter Wuille, February 2025
I certainly agree there is no urgency at present; but if (and only if) quantum computers capable of breaking cryptography actually become a reality, then the entire ecosystem has no choice but to disable the compromised spending schemes, and this must be done before such machines appear.
April 2025
I am not convinced about the feasibility of Ethan Heilman's proposal, but I am happy to see thinking and discussion in this direction.
July 2025
I believe that, at least in the medium term, the main quantum-related threat Bitcoin faces is not the actual appearance of cryptographically relevant quantum computers (CRQCs), but whether people believe they might appear soon.
I am not saying such a machine will never appear, but rather that the fear of its imminent appearance will have an impact earlier and more significantly. To be clear, I am not advocating for any specific action—whether a BIP, a timeline, a technical path, or even whether action should be taken.
Pieter participates in discussions about quantum risk, but he does not consider it an urgent matter. In his view, the problem lies more with people selling due to fear. (And this is indeed happening.)
Mara van der Laan, June 2015
In the most extreme case: if secp256k1 or SHA256 shows a clear weakness, or if practical quantum computing becomes powerful enough to factor discrete logarithms of that scale, I have no doubt that everyone would agree to introduce new cryptographic algorithms.
Mara, who served as a Bitcoin Core maintainer for a long time, then retired and returned. She mentioned the quantum issue in an earlier article but did not clearly state whether she believes there is a risk.
Peter Todd, July 2025
Despite all the talk about progress in quantum computing hardware, the fact remains: no one is close to demonstrating a quantum computer with cryptographically relevant capabilities. The cryptographically relevant capabilities of real hardware are almost laughable.
Whether they are physically feasible is still unknown; outside of some physics circles that want to sell you quantum computers or research funding, the mainstream view is that they do not conform to physical reality.
Adam Back, November 2025
Maybe 20–40 years, or it might never happen. Quantum-safe signatures already exist; NIST standardized SLH-DSA last year. Bitcoin can gradually introduce them as evaluations progress, preparing well before cryptographically relevant quantum computers appear.
Although the institution led by Adam Back does conduct post-quantum research, his personal assessment of the risk is: at least several decades away, no need to worry at all. He even publicly dismissed my concerns as FUD.
In my view, this attitude undermines the credibility of his institution's research results—if the CEO is making such remarks, I find it hard to understand how Blockstream's research can be used to prove that "developers are worried about quantum risk."
Gloria Zhao, August 2024
I think people sometimes worry about quantum computers, and this worry is indeed more interesting on a 30–50 year timescale than worrying about AI attacking Bitcoin.
Greg Maxwell, December 2025
Greg has discussed post-quantum signatures in a few exchanges but has not indicated his assessment of the risk. (I even went through his complete Reddit history.) Given his usually strong opinions, this silence is quite unusual.
Jonas Nick, February 2025
Thank you for your work on BIP360. I think now is a good time to develop and discuss specific post-quantum schemes.
Fortunately, Jonas is one of the most active post-quantum researchers in the Bitcoin community and has published papers on hash-based post-quantum signatures.
Anthony Towns discussed quantum attacks in 2018 but did not make a clear judgment on the risk.
Andrew Poelstra has not publicly commented on the risk but stated in 2021 that Taproot would not introduce quantum vulnerability.
To my knowledge, Alex Morcos, Michael Ford, and Marco Falke have never publicly mentioned quantum risk, so I infer they are not concerned (please correct me if wrong).
Summary
Overall, most of the most influential Bitcoin developers have not even acknowledged quantum risk. Those few who acknowledge it (except Jonas Nick) generally consider it theoretical, distant, or not actionable. Peter Todd and Adam Back explicitly deny the risk. Pieter Wuille acknowledges the problem exists, participates in discussions, but clearly states it is not a current risk or priority.
And without the nod from these people, any Bitcoin upgrade will fail.
The current conclusion is very simple: the most influential Bitcoin developers do not care about quantum risk.
Views of Other Bitcoin Developers
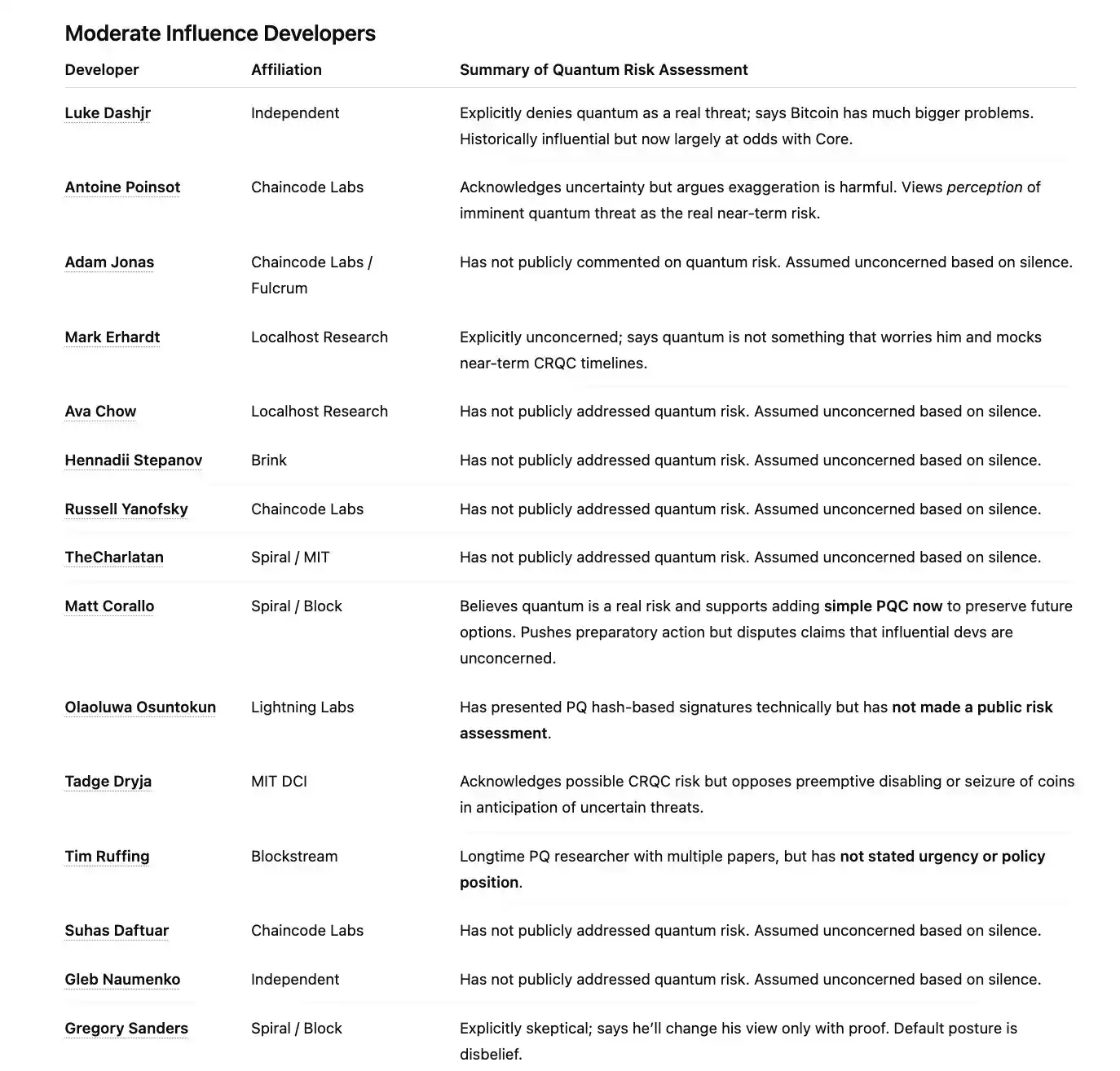
Luke Dashjr, December 2025
Quantum is not a real threat. Bitcoin has bigger problems to solve.
Luke clearly states he does not consider quantum a threat. He was historically a more influential and active Bitcoin developer, although now he is at odds with the Core system.
Matt Corallo, March 2025
(In response to Jameson's "Against Allowing Quantum Recovery of Bitcoin") I think this provides strong motivation for us to do "simple post-quantum cryptography (PQC)" today—while we don't need to decide now on the thorny issue of "whether to take over non-PQC coins," we want to preserve the option to do so in the future. For this option to be practically feasible, wallets must start embedding PQC public keys in their outputs at least ten years before the "takeover" happens; any longer lead time would give us an important safety margin. Therefore, now seems like the time to add the simplest form of PQC we can—add a most basic P_HASHBASEDSIG (likely SPHINCS+) to tapscript, so that wallets can hide PQC keys (including multisig) in their taptrees.
Matt Corallo does care and does believe there is a risk. But he explicitly denies my view that "the most important developers don't care," and calls my criticism "FUD." Perhaps Matt has some internal information I don't: maybe privately, developers are anxious about the quantum issue. But publicly, they act as if there is no risk at all.
Robin Linus, July 2025
Dogs are scarier than quantum computers.
Robin is the author of BitVM and a respected researcher in the field.
Mark Erhardt (Murch), November 2025
Of all the things that might keep me up at night, quantum computers are absolutely not one of them.
Most people who think the quantum threat is imminent are often just trying to raise more funds to "burn" on their research.
If we actually see CRQC within 20 years, feel free to laugh at me.
Antoine Poinsot, March 2025
(In response to my statement about "influential BTC developers downplaying the threat") I think this exaggeration weakens your (otherwise reasonable) point about "uncertainty."
It also exacerbates what I believe is the real threat that exists in the next decade: the perception among important stakeholders that the quantum threat is imminent.
Olaoluwa Osuntokun (roasbeef), July 2025
Laolu gave a talk on hash-based post-quantum signatures at the Presidio Bitcoin Quantum Summit. He stayed entirely at the technical level and did not assess the degree of risk.
Tadge Dryja, July 2025
(In response to Jameson's post-quantum proposal) Sure, CRQC could pose a risk. But this proposal goes in the opposite direction: preemptively disabling important features and even pre-destroying coins for something that might never happen.
Tim Ruffing, July 2025
Tim published a paper titled "Post-Quantum Security of Taproot as a Commitment Scheme." But to my knowledge, he has not directly commented on the risk itself. Credit to him, he started this kind of research early, even publishing a paper on post-quantum confidential transactions in 2017.
Gregory Sanders (instagibbs), December 2025
(In response to Scott Aaronson's comments on increasing quantum risk) The evidence will speak for itself; I'll change my tune then. Until then, I remain skeptical.
Jeremy Rubin, July 2021
An anecdote: Satoshi Nakamoto removed Bitcoin's post-quantum security in a hard fork in 2010.
The good news: by re-enabling OP_CAT or similar mechanisms, Bitcoin can become quantum-safe again.
Jeremy has been concerned about the quantum issue longer than most.
Amiti Uttarwar, January 2026
I find the discussion about the quantum threat very interesting. There are several people I consider very smart and long-time participants in the discussion who believe quantum poses an existential threat to Bitcoin.
Augustin Cruz, February 2025
In 2025, Augustin released a quantum migration proposal called QRAMP, but it was later deleted.
Mikhail Kudinov, 2025
Mikhail co-authored "Hash-Based Signature Schemes for Bitcoin" with Jonas Nick. His research agenda focuses mainly on post-quantum cryptography, so it is reasonable to assume he is very concerned about it.
Ethan Heilman, February 2025
I firmly believe that Bitcoin must migrate to post-quantum signatures in the near future.
Ethan has proposed several post-quantum schemes for Bitcoin and recently became one of the signatories of BIP360. He is one of the staunchest advocates for the post-quantum transition.
Jameson Lopp, July 2025
We want to protect the value of the UTXO set and minimize the incentive for quantum attacks. Bitcoin has never before faced an existential threat to its cryptographic primitives. A successful quantum attack would cause severe economic chaos and disruption to the entire ecosystem. NIST approved three post-quantum signature schemes for production use in 2024; some academic roadmaps even estimate that cryptographically relevant quantum computers could appear as early as 2027–2030.
Jameson has also been very active in sounding the alarm on quantum risk: both pushing for formal migration plans and driving public discussion around "what will happen to Satoshi's coins." Although he is not strictly a Core developer, he is undoubtedly one of the most vocal advocates for the transition.
Jonas Schnelli, December 2025
(In response to a tweet "Quantum computers aren't coming tomorrow") "All those predicting quantum doomsday, look at this article."
Jonas is an influential former Core maintainer who has now left Bitcoin development. He tends to downplay the risk.
Anthony Milton
Anthony is a low-profile but very active Bitcoin post-quantum researcher. He co-authored Chaincode's important report "Bitcoin and Quantum Computing" and runs PQ-Bitcoin.org, advocating for Bitcoin upgrades.
Clara Shikhelman
Clara is the head of research at Chaincode, co-authored the quantum report with Anthony Milton, and also co-runs PQ-Bitcoin with him.
Hunter Beast, December 2025
Industry roadmaps led by companies like IBM, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Intel, etc., indicate that quantum computers could break the ECDSA cryptographic system used for Bitcoin public-private key encryption within 2–5 years.
Hunter is the lead researcher for BIP360—currently the only named BIP explicitly aimed at facilitating quantum migration.
Influential figures who have not recently expressed views on quantum risk
Satoshi Nakamoto (last discussed: 2010)
Gavin Andresen (last discussed: 2010)
Hal Finney
Mara Van Der Laan (last discussed: 2015)
Marco Falke
Michael Ford (fanquake)
Hennadii Stepanov (hebasto)
Ryan Yanofsky (ryanofsky)
TheCharlatan
Alex Morcos
Ava Chow (last discussed: 2019)
Suhas Daftuar
Neha Narula
Samuel Dobson (meshcollider)
Rusty Russell
Gleb Naumenko
Cory Fields (cfields)
Overall Question: How Does the Bitcoin Developer Community as a Whole View Quantum Risk?
Based on my initial list of developers ranked by influence, and the public statements compiled above, we can now finally answer this question: when weighted by influence, how concerned are Bitcoin developers overall about quantum risk?
This is the conclusion to be drawn next.
Unfortunately, those at the very top, the key developers who truly decide whether Bitcoin will be updated, almost unanimously do not believe there is an imminent threat, with Jonas Nick being the only exception.
As the veritable "number one" key developer, Pieter Wuille has participated in discussions about the quantum issue multiple times, but he also believes there is no realistic risk at present.
Among developers with medium influence, the positions are quite diverse. On one hand, there is a group of researchers focused on quantum issues, such as Hunter Beast, Jameson Lopp, Clara Shikhelman, Anthony Milton, Ethan Heilman, Mikhail Kudinov, Augustin Cruz, Laolu, and Tim Ruffing.
On the other hand, there are also Core maintainers with actual power who remain silent on this threat; or well-known developers—like Luke Dashjr, Greg Sanders, Jonas Schnelli, or Tadge Dryja—who explicitly downplay or even deny quantum risk.
Although the work done by researchers like Hunter Beast, Anthony Milton, Jonas Nick, and Jameson Lopp is crucial, these results have not gained any substantive traction among the top-tier, elite "gatekeeping" developers. Don't believe it? Just look at the reaction on the mailing list when Hunter announced a major update to BIP360—only one reply. The roadmap proposed by Hunter also received only polite responses, with no follow-up action. Nothing will happen until the most influential developers formally endorse a proposal.
Conclusion
If you've read this far, the conclusion should be very clear: among the group of developers who truly decide whether the protocol changes, the quantum issue is seen as theoretical, distant, and even speculative, rather than a real, ongoing problem that requires engineering solutions.
Peter Todd, Adam Back, and Luke Dashjr explicitly deny its feasibility or real-world relevance; Pieter Wuille, Gloria Zhao, and Adam Back define the quantum issue as a concern to be faced at least 30–50 years from now; Van der Laan, Poelstra, Maxwell, Towns, Morcos, Falke, and others have either never stated a position or refused to participate in the discussion publicly.
Among the most important group, only Jonas Nick has explicitly expressed concern.
Serious concern exists below the line of power. Researchers like Heilman, Shikhelman, and Milton are seriously engaged in this work; Lopp is also persistently and rationally pushing the discussion—for which I genuinely give credit. Hunter Beast and his team are the ones investing the most on the practical side, trying to address one specific aspect (Taproot signature quantum vulnerability) through a named BIP. But so far, BIP360 has been met with complete indifference from the "opinion makers."
Do not be misled by the statements of Adam Back or Matt Corallo. Among the most influential Bitcoin developers, there is indeed a pathological indifference. Although there are a few bright spots, overall, quantum migration is clearly not a priority for Bitcoin Core and its main development funding organizations.