Authors: Li Hailun, Su Yang
On January 6th, Beijing time, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang, clad in his signature leather jacket, once again took the main stage at CES 2026.
At CES 2025, NVIDIA showcased the mass-produced Blackwell chip and a full-stack physical AI technology suite. During the event, Huang emphasized that an "era of Physical AI" was dawning. He painted a future full of imagination: autonomous vehicles with reasoning capabilities, robots that can understand and think, and AI Agents capable of handling long-context tasks involving millions of tokens.
A year has passed in a flash, and the AI industry has undergone significant evolution and change. Reviewing these changes at the launch event, Huang specifically highlighted open-source models.
He stated that open-source reasoning models like DeepSeek R1 have made the entire industry realize: when true openness and global collaboration kick in, the diffusion speed of AI becomes extremely rapid. Although open-source models still lag behind the most advanced models by about six months in overall capability, they close the gap every six months, and their downloads and usage have already seen explosive growth.
Compared to 2025's focus more on vision and possibilities, this time NVIDIA began systematically addressing the question of "how to achieve it":围绕推理型 AI (focusing on reasoning AI), it is bolstering the compute, networking, and storage infrastructure required for long-term operation, significantly reducing inference costs, and embedding these capabilities directly into real-world scenarios like autonomous driving and robotics.
Huang's CES keynote this year unfolded along three main lines:
● At the system and infrastructure level, NVIDIA redesigned the compute, networking, and storage architecture around long-term inference needs. With the Rubin platform, NVLink 6, Spectrum-X Ethernet, and the Inference Context Memory Storage platform at the core, these updates directly target bottlenecks like high inference costs, difficulty in sustaining context, and scalability limitations, solving the problems of letting AI 'think a bit longer', 'afford to compute', and 'run persistently'.
● At the model level, NVIDIA placed Reasoning / Agentic AI at the core. Through models and tools like Alpamayo, Nemotron, and Cosmos Reason, it is pushing AI from "generating content" towards "continuous thinking", and from "one-time response models" to "agents that can work long-term".
● At the application and deployment level, these capabilities are being directly integrated into Physical AI scenarios like autonomous driving and robotics. Whether it's the Alpamayo-powered autonomous driving system or the GR00T and Jetson robotics ecosystem, they are driving scaled deployment through partnerships with cloud providers and enterprise platforms.
01 From Roadmap to Mass Production: Rubin's Full Performance Data Revealed for the First Time
At this CES, NVIDIA fully disclosed the technical details of the Rubin architecture for the first time.
In his speech, Huang started with the concept of Test-time Scaling. This concept can be understood as: making AI smarter isn't just about making it "study harder" during training anymore, but rather letting it "think a bit longer when encountering a problem".
In the past, improvements in AI capability relied mainly on throwing more compute power at the training stage, making models larger and larger; now, the new change is that even if the model stops growing, simply giving it a bit more time and compute power to think during each use can significantly improve the results.
How to make "AI thinking a bit longer" economically feasible? The Rubin architecture's next-generation AI computing platform is here to solve this problem.
Huang introduced it as a complete next-generation AI computing system, achieving a revolutionary drop in inference costs through the co-design of the Vera CPU, Rubin GPU, NVLink 6, ConnectX-9, BlueField-4, and Spectrum-6.
The NVIDIA Rubin GPU is the core chip responsible for AI compute in the Rubin architecture, aiming to significantly reduce the unit cost of inference and training.
Simply put, the Rubin GPU's core mission is to "make AI cheaper and smarter to use".
The core capability of the Rubin GPU lies in: the same GPU can handle more work. It can process more inference tasks at once, remember longer context, and communicate faster with other GPUs. This means many scenarios that previously required "stacking multiple cards" can now be accomplished with fewer GPUs.
The result is that inference is not only faster, but also significantly cheaper.
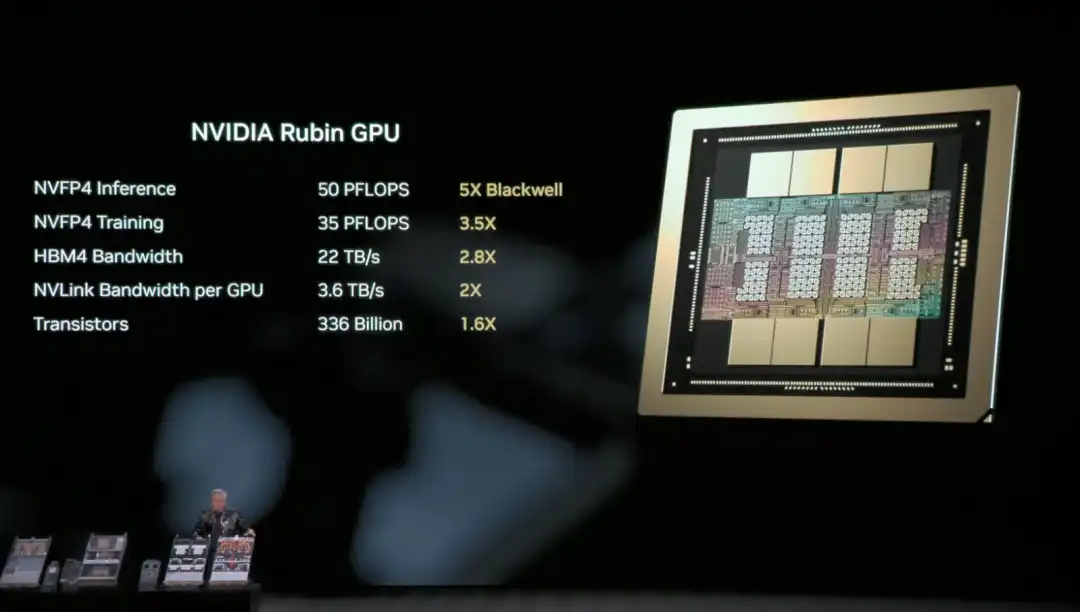
Huang recapped the hardware specs of the Rubin architecture's NVL72 for the audience: it contains 220 trillion transistors, with a bandwidth of 260 TB/s, and is the industry's first platform supporting rack-scale confidential computing.
Overall, compared to Blackwell, the Rubin GPU achieves a generational leap in key metrics: NVFP4 inference performance increases to 50 PFLOPS (5x), training performance to 35 PFLOPS (3.5x), HBM4 memory bandwidth to 22 TB/s (2.8x), and single GPU NVLink interconnect bandwidth doubles to 3.6 TB/s.
These improvements work together to enable a single GPU to handle more inference tasks and longer context, fundamentally reducing the reliance on the number of GPUs.
The Vera CPU is a core component designed specifically for data movement and Agentic processing, featuring 88 NVIDIA-designed Olympus cores, equipped with 1.5 TB of system memory (3x that of the previous Grace CPU), and achieving coherent memory access between CPU and GPU through 1.8 TB/s NVLink-C2C technology.
Unlike traditional general-purpose CPUs, Vera focuses on data scheduling and multi-step reasoning logic processing in AI inference scenarios, essentially acting as the system coordinator that enables "AI thinking a bit longer" to run efficiently.
NVLink 6, with its 3.6 TB/s bandwidth and in-network computing capability, allows the 72 GPUs in the Rubin architecture to work together like a single super GPU, which is key infrastructure for reducing inference costs.
This way, the data and intermediate results needed by AI during inference can quickly circulate between GPUs, without repeatedly waiting, copying, or recalculating.
In the Rubin architecture, NVLink-6 handles internal collaborative computing between GPUs, BlueField-4 handles context and data scheduling, and ConnectX-9 undertakes the system's high-speed external network connectivity. It ensures the Rubin system can communicate efficiently with other racks, data centers, and cloud platforms, a prerequisite for the smooth operation of large-scale training and inference tasks.
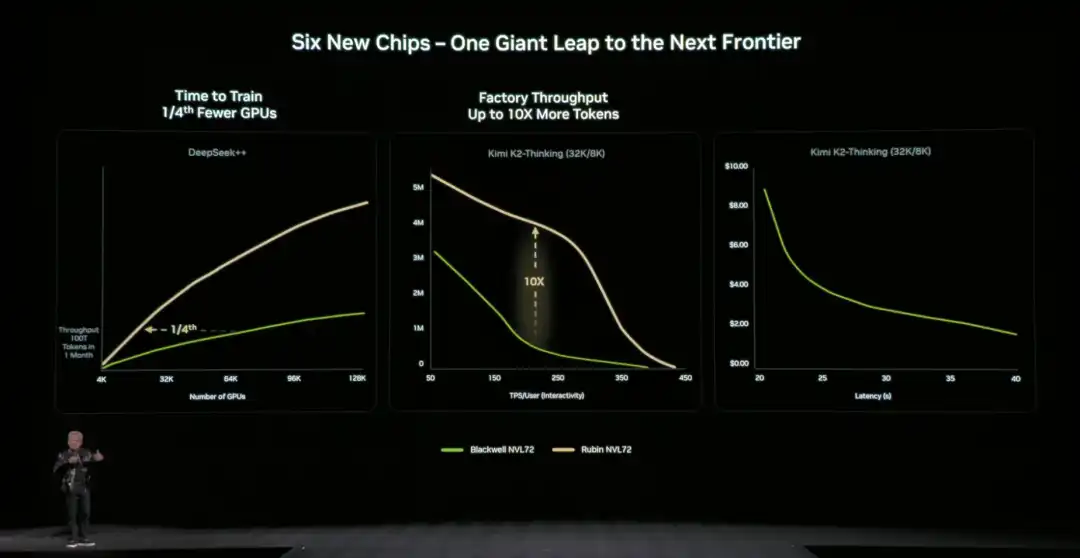
Compared to the previous generation architecture, NVIDIA also provided specific,直观的数据 (intuitive data): compared to the NVIDIA Blackwell platform, it can reduce token costs in the inference phase by up to 10 times, and reduce the number of GPUs required for training Mixture of Experts (MoE) models to 1/4 of the original.
NVIDIA officially stated that Microsoft has already committed to deploying hundreds of thousands of Vera Rubin chips in its next-generation Fairwater AI super factory, and cloud service providers like CoreWeave will offer Rubin instances in the second half of 2026. This infrastructure for "letting AI think a bit longer" is moving from technical demonstration to scaled commercial use.
02 How is the "Storage Bottleneck" Solved?
Letting AI "think a bit longer" also faces a key technical challenge: where should the context data be stored?
When AI handles complex tasks requiring multi-turn dialogue or multi-step reasoning, it generates a large amount of context data (KV Cache). Traditional architectures either cram it into expensive and capacity-limited GPU memory or put it in ordinary storage (which is too slow to access). If this "storage bottleneck" isn't solved, even the most powerful GPU will be hampered.
To address this issue, NVIDIA fully disclosed the BlueField-4 powered Inference Context Memory Storage Platform for the first time at this CES. The core goal is to create a "third layer" between GPU memory and traditional storage. It's fast enough, has ample capacity, and can support AI's long-term operation.
From a technical implementation perspective, this platform isn't the result of a single component working alone, but rather a set of co-designed elements:
- BlueField-4 is responsible for accelerating the management and access of context data at the hardware level, reducing data movement and system overhead;
- Spectrum-X Ethernet provides high-performance networking, supporting high-speed data sharing based on RDMA;
- Software components like DOCA, NIXL, and Dynamo are responsible for optimizing scheduling, reducing latency, and improving overall throughput at the system level.
We can understand this platform's approach as extending the context data, which originally could only reside in GPU memory, to an independent, high-speed, shareable "memory layer". This一方面 (on one hand) relieves pressure on the GPU, and另一方面 (on the other hand) allows for rapid sharing of this context information between multiple nodes and multiple AI agents.
In terms of actual效果 (effects), the data provided by NVIDIA官方 (officially) is: in specific scenarios, this method can increase the number of tokens processed per second by up to 5 times, and achieve同等水平的 (equivalent levels of) energy efficiency optimization.
Huang emphasized多次 (repeatedly) during the presentation that AI is evolving from "one-time dialogue chatbots" to true intelligent collaborators: they need to understand the real world, reason continuously, call tools to complete tasks, and retain both short-term and long-term memory. This is the core characteristic of Agentic AI. The Inference Context Memory Storage Platform is designed precisely for this long-running,反复思考的 (repeatedly thinking) form of AI. By expanding context capacity and speeding up cross-node sharing, it makes multi-turn conversations and multi-agent collaboration more stable, no longer "slowing down the longer it runs".
03 The New Generation DGX SuperPOD: Enabling 576 GPUs to Work Together
NVIDIA announced the new generation DGX SuperPOD (Super Pod) based on the Rubin architecture at this CES, expanding Rubin from a single rack to a complete data center solution.
What is a DGX SuperPOD?
If the Rubin NVL72 is a "super rack" containing 72 GPUs, then the DGX SuperPOD connects multiple such racks together to form a larger-scale AI computing cluster. This released version consists of 8 Vera Rubin NVL72 racks, equivalent to 576 GPUs working together.
When AI task scales continue to expand, the 576 GPUs of a single SuperPOD might not be enough. For example, training ultra-large-scale models, simultaneously serving thousands of Agentic AI agents, or processing complex tasks requiring millions of tokens of context. This requires multiple SuperPODs working together, and the DGX SuperPOD is the standardized solution for this scenario.
For enterprises and cloud service providers, the DGX SuperPOD provides an "out-of-the-box" large-scale AI infrastructure solution. There's no need to figure out how to connect hundreds of GPUs, configure networks, manage storage, etc., themselves.
The five core components of the new generation DGX SuperPOD:
○ 8 Vera Rubin NVL72 Racks - The core providing computing power, 72 GPUs per rack, 576 GPUs total;
○ NVLink 6 Expansion Network - Allows the 576 GPUs across these 8 racks to work together like one超大 (super large) GPU;
○ Spectrum-X Ethernet Expansion Network - Connects different SuperPODs, and to storage and external networks;
○ Inference Context Memory Storage Platform - Provides shared context data storage for long-running inference tasks;
○ NVIDIA Mission Control Software - Manages scheduling, monitoring, and optimization of the entire system.
With this upgrade, the foundation of the SuperPOD is the DGX Vera Rubin NVL72 rack-scale system at its core. Each NVL72 is itself a complete AI supercomputer, internally connecting 72 Rubin GPUs via NVLink 6, capable of handling large-scale inference and training tasks within a single rack. The new DGX SuperPOD consists of multiple NVL72 units, forming a system-level cluster capable of long-term operation.
When the compute scale expands from "single rack" to "multi-rack", new bottlenecks emerge: how to stably and efficiently传输海量数据 (transfer massive amounts of data) between racks.围绕这一问题 (Around this issue), NVIDIA simultaneously announced the new generation Ethernet switch based on the Spectrum-6 chip at this CES, and introduced "Co-Packaged Optics" (CPO) technology for the first time.
Simply put, this involves packaging the originally pluggable optical modules directly next to the switch chip, reducing the signal transmission distance from meters to millimeters, thereby significantly reducing power consumption and latency, and also improving the overall stability of the system.
04 NVIDIA's Open Source AI "Full Stack": Everything from Data to Code
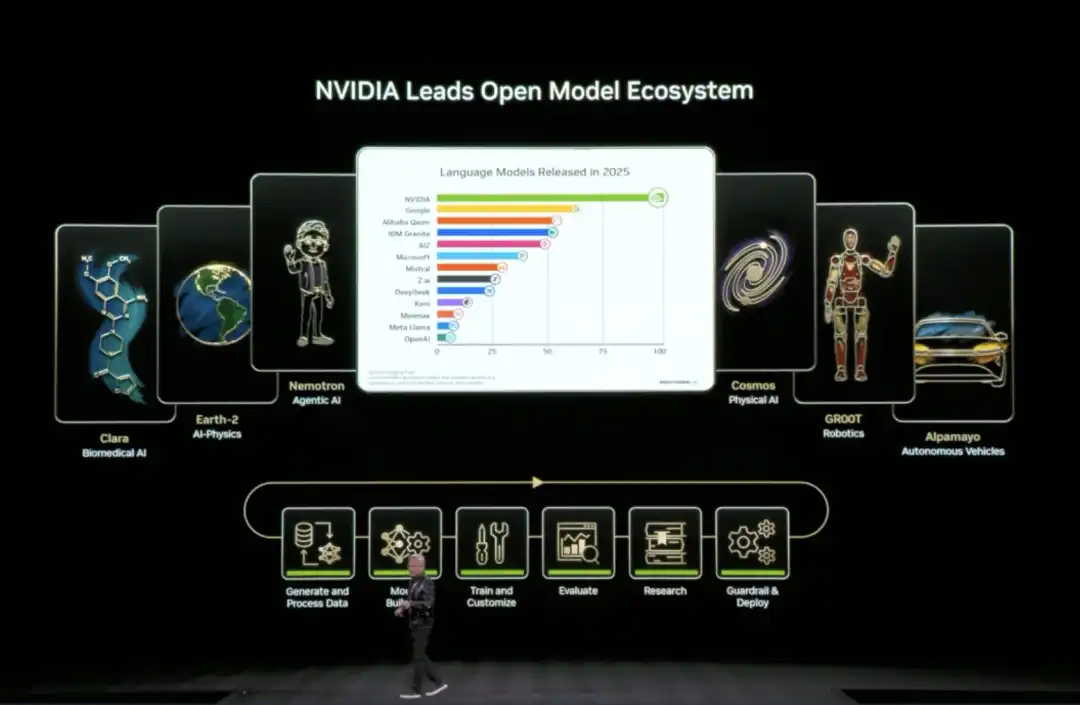
At this CES, Huang announced the expansion of its open-source model ecosystem (Open Model Universe), adding and updating a series of models, datasets, code libraries, and tools. This ecosystem covers six areas: Biomedical AI (Clara), AI Physics Simulation (Earth-2), Agentic AI (Nemotron), Physical AI (Cosmos), Robotics (GR00T), and Autonomous Driving (Alpamayo).
Training an AI model requires not just compute power, but also high-quality datasets, pre-trained models, training code, evaluation tools, and a whole set of infrastructure. For most companies and research institutions, building these from scratch is too time-consuming.
Specifically, NVIDIA has open-sourced six layers of content: compute platforms (DGX, HGX, etc.), training datasets for various domains, pre-trained foundation models, inference and training code libraries, complete training process scripts, and end-to-end solution templates.
The Nemotron series was a key focus of this update, covering four application directions.
In the reasoning direction, it includes small-scale reasoning models like Nemotron 3 Nano, Nemotron 2 Nano VL, as well as reinforcement learning training tools like NeMo RL and NeMo Gym. In the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) direction, it provides Nemotron Embed VL (vector embedding model), Nemotron Rerank VL (re-ranking model), relevant datasets, and the NeMo Retriever Library. In the safety direction, there is the Nemotron Content Safety model and its配套数据集 (matching dataset), and the NeMo Guardrails library.
In the speech direction, it includes Nemotron ASR for automatic speech recognition, the Granary Dataset for speech, and the NeMo Library for speech processing. This means if a company wants to build an AI customer service system with RAG, it doesn't need to train its own embedding and re-ranking models; it can directly use the code NVIDIA has already trained and open-sourced.
05 Physical AI Domain Moves Towards Commercial Deployment
The Physical AI domain also saw model updates—Cosmos for understanding and generating videos of the physical world, the general-purpose robotics foundation model Isaac GR00T, and the vision-language-action model for autonomous driving, Alpamayo.
Huang claimed at CES that the "ChatGPT moment" for Physical AI is approaching, but there are many challenges: the physical world is too complex and variable, collecting real data is slow and expensive, and there's never enough.
What's the solution? Synthetic data is one path. Hence, NVIDIA introduced Cosmos.
This is an open-source foundational model for the physical AI world, already pre-trained on massive amounts of video, real driving and robotics data, and 3D simulation. It can understand how the world works and connect language, images, 3D, and actions.
Huang stated that Cosmos can achieve several physical AI skills, such as generating content, performing reasoning, and predicting trajectories (even if only given a single image). It can generate realistic videos based on 3D scenes, generate physically plausible motion based on driving data, and even generate panoramic videos from simulators, multi-camera footage, or text descriptions. It can even还原 (recreate) rare scenarios.
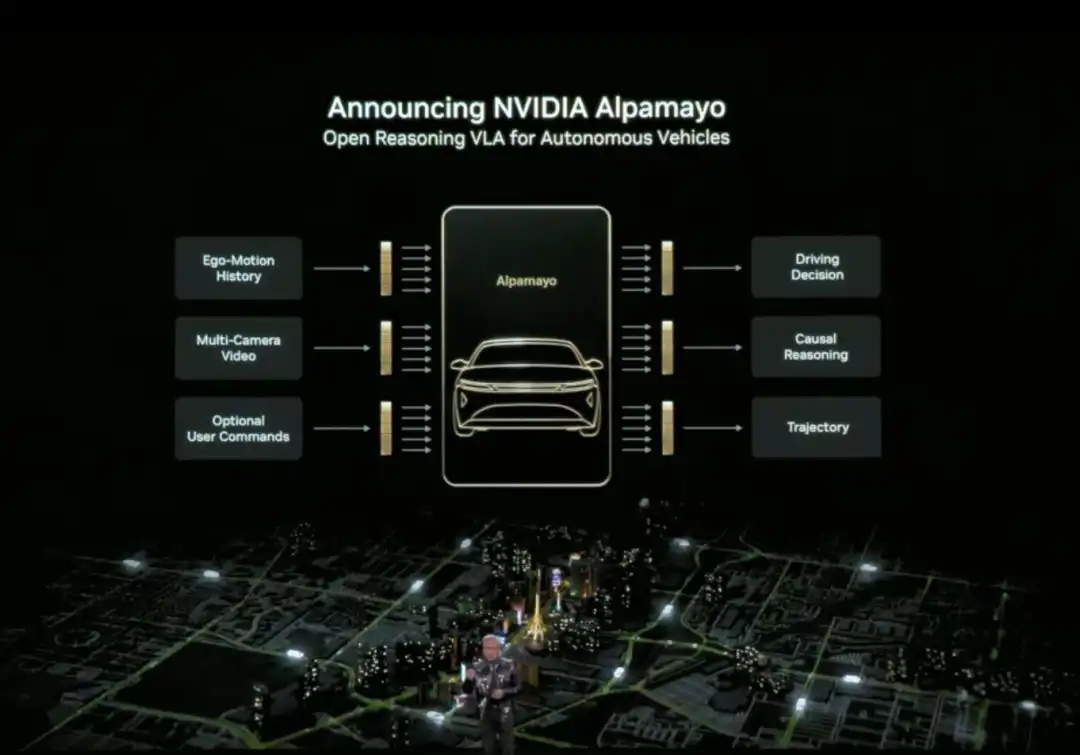
Huang also officially released Alpamayo. Alpamayo is an open-source toolchain for the autonomous driving domain, and the first open-source vision-language-action (VLA) reasoning model. Unlike previous open-sourcing of only code, NVIDIA this time open-sourced the complete development resources from data to deployment.
Alpamayo's biggest breakthrough is that it is a "reasoning" autonomous driving model. Traditional autonomous driving systems follow a "perception-planning-control" pipeline architecture—see a red light and brake, see a pedestrian and slow down, following preset rules. Alpamayo introduces "reasoning" capability, understanding causal relationships in complex scenes, predicting the intentions of other vehicles and pedestrians, and even handling decisions requiring multi-step thinking.
For example, at an intersection, it doesn't just recognize "there's a car ahead", but can reason "that car might be turning left, so I should wait for it to go first". This capability upgrades autonomous driving from "driving by rules" to "thinking like a human".
Huang announced that the NVIDIA DRIVE system has officially entered the mass production phase, with the first application being the new Mercedes-Benz CLA, planned to hit US roads in 2026. This vehicle will be equipped with an L2++ level autonomous driving system, adopting a hybrid architecture of "end-to-end AI model + traditional pipeline".
The robotics field also saw substantial progress.
Huang stated that leading global robotics companies, including Boston Dynamics, Franka Robotics, LEM Surgical, LG Electronics, Neura Robotics, and XRlabs, are developing products based on the NVIDIA Isaac platform and the GR00T foundation model, covering various fields from industrial robots and surgical robots to humanoid robots and consumer robots.
During the launch event, Huang stood in front of a stage filled with robots of different forms and用途 (purposes), displayed on a tiered platform: from humanoid robots, bipedal and wheeled service robots, to industrial robotic arms, engineering machinery, drones, and surgical assist devices, presenting a "robotics ecosystem landscape".
From Physical AI applications to the Rubin AI computing platform, to the Inference Context Memory Storage platform and the open-source AI "full stack".
These actions showcased by NVIDIA at CES constitute NVIDIA's narrative for推理时代 AI 基础设施 (AI infrastructure for the reasoning era). As Huang repeatedly emphasized, when Physical AI needs to think continuously, run persistently, and truly enter the real world, the problem is no longer just about whether there's enough compute power, but about who can actually build the entire system.
At CES 2026, NVIDIA has provided an answer.
Perguntas relacionadas
QWhat are the three main topics of Jensen Huang's CES 2026 keynote?
AThe three main topics are: 1) Reconstructing computing, networking, and storage architecture around long-term inference needs with the Rubin platform, NVLink 6, Spectrum-X Ethernet, and the inference context memory storage platform. 2) Placing reasoning/agentic AI at the core through models and tools like Alpamayo, Nemotron, and Cosmos Reason. 3) Directly applying these capabilities to physical AI scenarios like autonomous driving and robotics.
QWhat is the key innovation of the Rubin GPU architecture and its primary goal?
AThe key innovation of the Rubin GPU architecture is its ability to handle more inference tasks and longer context within a single GPU, facilitated by a significant performance leap over Blackwell. Its primary goal is to 'make AI cheaper and smarter to use' by dramatically reducing the cost of inference and the number of GPUs required for many tasks.
QWhat problem does the Inference Context Memory Storage Platform solve, and what are its core components?
AIt solves the 'storage bottleneck' problem, where context data (KV Cache) from multi-step AI reasoning tasks traditionally had to be stored in expensive, limited GPU memory or slow conventional storage. Its core components are the BlueField-4 DPU (for hardware-accelerated data management), Spectrum-X Ethernet (for high-performance networking), and software components like DOCA, NIXL, and Dynamo for system optimization.
QWhat major advancement did NVIDIA announce for the autonomous driving sector?
ANVIDIA announced the official entry of its DRIVE system into mass production, with the first application being the new Mercedes-Benz CLA, planned for US roads in 2026. They also open-sourced Alpamayo, the first visual-language-action (VLA) reasoning model for autonomous driving, which introduces causal reasoning and multi-step decision-making capabilities.
QWhat is the significance of the new DGX SuperPOD based on the Rubin architecture?
AThe new DGX SuperPOD scales the Rubin architecture from a single rack (NVL72 with 72 GPUs) to a data-center-scale solution. Composed of 8 NVL72 racks for a total of 576 GPUs, it provides an 'out-of-the-box' massive AI computing cluster for training ultra-large models or serving thousands of Agentic AI agents, managed by the NVIDIA Mission Control software.
Leituras Relacionadas
Trading
Artigos em Destaque
O que é $S$
Compreender o SPERO: Uma Visão Abrangente Introdução ao SPERO À medida que o panorama da inovação continua a evoluir, o surgimento de tecnologias web3 e projetos de criptomoeda desempenha um papel fundamental na formação do futuro digital. Um projeto que tem atraído atenção neste campo dinâmico é o SPERO, denotado como SPERO,$$s$. Este artigo tem como objetivo reunir e apresentar informações detalhadas sobre o SPERO, para ajudar entusiastas e investidores a compreender as suas bases, objetivos e inovações nos domínios web3 e cripto. O que é o SPERO,$$s$? O SPERO,$$s$ é um projeto único dentro do espaço cripto que procura aproveitar os princípios da descentralização e da tecnologia blockchain para criar um ecossistema que promove o envolvimento, a utilidade e a inclusão financeira. O projeto é concebido para facilitar interações peer-to-peer de novas maneiras, proporcionando aos utilizadores soluções e serviços financeiros inovadores. No seu núcleo, o SPERO,$$s$ visa capacitar indivíduos ao fornecer ferramentas e plataformas que melhoram a experiência do utilizador no espaço das criptomoedas. Isso inclui a possibilidade de métodos de transação mais flexíveis, a promoção de iniciativas impulsionadas pela comunidade e a criação de caminhos para oportunidades financeiras através de aplicações descentralizadas (dApps). A visão subjacente do SPERO,$$s$ gira em torno da inclusão, visando fechar lacunas dentro das finanças tradicionais enquanto aproveita os benefícios da tecnologia blockchain. Quem é o Criador do SPERO,$$s$? A identidade do criador do SPERO,$$s$ permanece algo obscura, uma vez que existem recursos publicamente disponíveis limitados que fornecem informações detalhadas sobre o(s) seu(s) fundador(es). Esta falta de transparência pode resultar do compromisso do projeto com a descentralização—uma ética que muitos projetos web3 partilham, priorizando contribuições coletivas em vez de reconhecimento individual. Ao centrar as discussões em torno da comunidade e dos seus objetivos coletivos, o SPERO,$$s$ incorpora a essência do empoderamento sem destacar indivíduos específicos. Assim, compreender a ética e a missão do SPERO é mais importante do que identificar um criador singular. Quem são os Investidores do SPERO,$$s$? O SPERO,$$s$ é apoiado por uma diversidade de investidores que vão desde capitalistas de risco a investidores-anjo dedicados a promover a inovação no setor cripto. O foco desses investidores geralmente alinha-se com a missão do SPERO—priorizando projetos que prometem avanço tecnológico social, inclusão financeira e governança descentralizada. Essas fundações de investidores estão tipicamente interessadas em projetos que não apenas oferecem produtos inovadores, mas que também contribuem positivamente para a comunidade blockchain e os seus ecossistemas. O apoio desses investidores reforça o SPERO,$$s$ como um concorrente notável no domínio em rápida evolução dos projetos cripto. Como Funciona o SPERO,$$s$? O SPERO,$$s$ emprega uma estrutura multifacetada que o distingue de projetos de criptomoeda convencionais. Aqui estão algumas das características-chave que sublinham a sua singularidade e inovação: Governança Descentralizada: O SPERO,$$s$ integra modelos de governança descentralizada, capacitando os utilizadores a participar ativamente nos processos de tomada de decisão sobre o futuro do projeto. Esta abordagem promove um sentido de propriedade e responsabilidade entre os membros da comunidade. Utilidade do Token: O SPERO,$$s$ utiliza o seu próprio token de criptomoeda, concebido para servir várias funções dentro do ecossistema. Esses tokens permitem transações, recompensas e a facilitação de serviços oferecidos na plataforma, melhorando o envolvimento e a utilidade gerais. Arquitetura em Camadas: A arquitetura técnica do SPERO,$$s$ suporta modularidade e escalabilidade, permitindo a integração contínua de funcionalidades e aplicações adicionais à medida que o projeto evolui. Esta adaptabilidade é fundamental para manter a relevância no panorama cripto em constante mudança. Envolvimento da Comunidade: O projeto enfatiza iniciativas impulsionadas pela comunidade, empregando mecanismos que incentivam a colaboração e o feedback. Ao nutrir uma comunidade forte, o SPERO,$$s$ pode melhor atender às necessidades dos utilizadores e adaptar-se às tendências do mercado. Foco na Inclusão: Ao oferecer taxas de transação baixas e interfaces amigáveis, o SPERO,$$s$ visa atrair uma base de utilizadores diversificada, incluindo indivíduos que anteriormente podem não ter participado no espaço cripto. Este compromisso com a inclusão alinha-se com a sua missão abrangente de empoderamento através da acessibilidade. Cronologia do SPERO,$$s$ Compreender a história de um projeto fornece insights cruciais sobre a sua trajetória de desenvolvimento e marcos. Abaixo está uma cronologia sugerida que mapeia eventos significativos na evolução do SPERO,$$s$: Fase de Conceituação e Ideação: As ideias iniciais que formam a base do SPERO,$$s$ foram concebidas, alinhando-se de perto com os princípios de descentralização e foco na comunidade dentro da indústria blockchain. Lançamento do Whitepaper do Projeto: Após a fase conceitual, um whitepaper abrangente detalhando a visão, os objetivos e a infraestrutura tecnológica do SPERO,$$s$ foi lançado para atrair o interesse e o feedback da comunidade. Construção da Comunidade e Primeiros Envolvimentos: Esforços ativos de divulgação foram feitos para construir uma comunidade de primeiros adotantes e investidores potenciais, facilitando discussões em torno dos objetivos do projeto e angariando apoio. Evento de Geração de Tokens: O SPERO,$$s$ realizou um evento de geração de tokens (TGE) para distribuir os seus tokens nativos a apoiantes iniciais e estabelecer liquidez inicial dentro do ecossistema. Lançamento da dApp Inicial: A primeira aplicação descentralizada (dApp) associada ao SPERO,$$s$ foi lançada, permitindo que os utilizadores interagissem com as funcionalidades principais da plataforma. Desenvolvimento Contínuo e Parcerias: Atualizações e melhorias contínuas nas ofertas do projeto, incluindo parcerias estratégicas com outros players no espaço blockchain, moldaram o SPERO,$$s$ em um jogador competitivo e em evolução no mercado cripto. Conclusão O SPERO,$$s$ é um testemunho do potencial do web3 e das criptomoedas para revolucionar os sistemas financeiros e capacitar indivíduos. Com um compromisso com a governança descentralizada, o envolvimento da comunidade e funcionalidades inovadoras, abre caminho para um panorama financeiro mais inclusivo. Como em qualquer investimento no espaço cripto em rápida evolução, potenciais investidores e utilizadores são incentivados a pesquisar minuciosamente e a envolver-se de forma ponderada com os desenvolvimentos em curso dentro do SPERO,$$s$. O projeto demonstra o espírito inovador da indústria cripto, convidando a uma exploração mais aprofundada das suas inúmeras possibilidades. Embora a jornada do SPERO,$$s$ ainda esteja a desenrolar-se, os seus princípios fundamentais podem, de facto, influenciar o futuro de como interagimos com a tecnologia, as finanças e uns com os outros em ecossistemas digitais interconectados.
69 Visualizações TotaisPublicado em {updateTime}Atualizado em 2024.12.17
O que é AGENT S
Agent S: O Futuro da Interação Autónoma no Web3 Introdução No panorama em constante evolução do Web3 e das criptomoedas, as inovações estão constantemente a redefinir a forma como os indivíduos interagem com plataformas digitais. Um projeto pioneiro, o Agent S, promete revolucionar a interação humano-computador através do seu framework aberto e agente. Ao abrir caminho para interações autónomas, o Agent S visa simplificar tarefas complexas, oferecendo aplicações transformadoras em inteligência artificial (IA). Esta exploração detalhada irá aprofundar-se nas complexidades do projeto, nas suas características únicas e nas implicações para o domínio das criptomoedas. O que é o Agent S? O Agent S é um framework aberto e agente, especificamente concebido para abordar três desafios fundamentais na automação de tarefas computacionais: Aquisição de Conhecimento Específico de Domínio: O framework aprende inteligentemente a partir de várias fontes de conhecimento externas e experiências internas. Esta abordagem dupla capacita-o a construir um rico repositório de conhecimento específico de domínio, melhorando o seu desempenho na execução de tarefas. Planeamento ao Longo de Longos Horizontes de Tarefas: O Agent S emprega planeamento hierárquico aumentado por experiência, uma abordagem estratégica que facilita a decomposição e execução eficientes de tarefas intrincadas. Esta característica melhora significativamente a sua capacidade de gerir múltiplas subtarefas de forma eficiente e eficaz. Gestão de Interfaces Dinâmicas e Não Uniformes: O projeto introduz a Interface Agente-Computador (ACI), uma solução inovadora que melhora a interação entre agentes e utilizadores. Utilizando Modelos de Linguagem Multimodais de Grande Escala (MLLMs), o Agent S pode navegar e manipular diversas interfaces gráficas de utilizador de forma fluida. Através destas características pioneiras, o Agent S fornece um framework robusto que aborda as complexidades envolvidas na automação da interação humana com máquinas, preparando o terreno para uma infinidade de aplicações em IA e além. Quem é o Criador do Agent S? Embora o conceito de Agent S seja fundamentalmente inovador, informações específicas sobre o seu criador permanecem elusivas. O criador é atualmente desconhecido, o que destaca ou o estágio nascente do projeto ou a escolha estratégica de manter os membros fundadores em anonimato. Independentemente da anonimidade, o foco permanece nas capacidades e no potencial do framework. Quem são os Investidores do Agent S? Como o Agent S é relativamente novo no ecossistema criptográfico, informações detalhadas sobre os seus investidores e financiadores não estão explicitamente documentadas. A falta de informações disponíveis publicamente sobre as fundações de investimento ou organizações que apoiam o projeto levanta questões sobre a sua estrutura de financiamento e roteiro de desenvolvimento. Compreender o apoio é crucial para avaliar a sustentabilidade do projeto e o seu impacto potencial no mercado. Como Funciona o Agent S? No núcleo do Agent S reside uma tecnologia de ponta que lhe permite funcionar eficazmente em diversos ambientes. O seu modelo operacional é construído em torno de várias características-chave: Interação Humano-Computador Semelhante: O framework oferece planeamento avançado em IA, esforçando-se para tornar as interações com computadores mais intuitivas. Ao imitar o comportamento humano na execução de tarefas, promete elevar as experiências dos utilizadores. Memória Narrativa: Utilizada para aproveitar experiências de alto nível, o Agent S utiliza memória narrativa para acompanhar os históricos de tarefas, melhorando assim os seus processos de tomada de decisão. Memória Episódica: Esta característica fornece aos utilizadores orientações passo a passo, permitindo que o framework ofereça suporte contextual à medida que as tarefas se desenrolam. Suporte para OpenACI: Com a capacidade de funcionar localmente, o Agent S permite que os utilizadores mantenham o controlo sobre as suas interações e fluxos de trabalho, alinhando-se com a ética descentralizada do Web3. Fácil Integração com APIs Externas: A sua versatilidade e compatibilidade com várias plataformas de IA garantem que o Agent S possa integrar-se perfeitamente em ecossistemas tecnológicos existentes, tornando-o uma escolha apelativa para desenvolvedores e organizações. Estas funcionalidades contribuem coletivamente para a posição única do Agent S no espaço cripto, à medida que automatiza tarefas complexas e em múltiplos passos com mínima intervenção humana. À medida que o projeto evolui, as suas potenciais aplicações no Web3 podem redefinir a forma como as interações digitais se desenrolam. Cronologia do Agent S O desenvolvimento e os marcos do Agent S podem ser encapsulados numa cronologia que destaca os seus eventos significativos: 27 de Setembro de 2024: O conceito de Agent S foi lançado num artigo de pesquisa abrangente intitulado “Um Framework Agente Aberto que Usa Computadores como um Humano”, mostrando a base para o projeto. 10 de Outubro de 2024: O artigo de pesquisa foi disponibilizado publicamente no arXiv, oferecendo uma exploração aprofundada do framework e da sua avaliação de desempenho com base no benchmark OSWorld. 12 de Outubro de 2024: Uma apresentação em vídeo foi lançada, proporcionando uma visão visual das capacidades e características do Agent S, envolvendo ainda mais potenciais utilizadores e investidores. Estes marcos na cronologia não apenas ilustram o progresso do Agent S, mas também indicam o seu compromisso com a transparência e o envolvimento da comunidade. Pontos-Chave Sobre o Agent S À medida que o framework Agent S continua a evoluir, várias características-chave destacam-se, sublinhando a sua natureza inovadora e potencial: Framework Inovador: Concebido para proporcionar um uso intuitivo de computadores semelhante à interação humana, o Agent S traz uma abordagem nova à automação de tarefas. Interação Autónoma: A capacidade de interagir autonomamente com computadores através de GUI significa um avanço em direção a soluções computacionais mais inteligentes e eficientes. Automação de Tarefas Complexas: Com a sua metodologia robusta, pode automatizar tarefas complexas e em múltiplos passos, tornando os processos mais rápidos e menos propensos a erros. Melhoria Contínua: Os mecanismos de aprendizagem permitem que o Agent S melhore a partir de experiências passadas, aprimorando continuamente o seu desempenho e eficácia. Versatilidade: A sua adaptabilidade em diferentes ambientes operacionais, como OSWorld e WindowsAgentArena, garante que pode servir uma ampla gama de aplicações. À medida que o Agent S se posiciona no panorama do Web3 e das criptomoedas, o seu potencial para melhorar as capacidades de interação e automatizar processos significa um avanço significativo nas tecnologias de IA. Através do seu framework inovador, o Agent S exemplifica o futuro das interações digitais, prometendo uma experiência mais fluida e eficiente para os utilizadores em diversas indústrias. Conclusão O Agent S representa um ousado avanço na união da IA e do Web3, com a capacidade de redefinir a forma como interagimos com a tecnologia. Embora ainda esteja nas suas fases iniciais, as possibilidades para a sua aplicação são vastas e cativantes. Através do seu framework abrangente que aborda desafios críticos, o Agent S visa trazer interações autónomas para o primeiro plano da experiência digital. À medida que avançamos mais profundamente nos domínios das criptomoedas e da descentralização, projetos como o Agent S desempenharão, sem dúvida, um papel crucial na formação do futuro da tecnologia e da colaboração humano-computador.
142 Visualizações TotaisPublicado em {updateTime}Atualizado em 2025.01.14
Como comprar S
Bem-vindo à HTX.com!Tornámos a compra de Sonic (S) simples e conveniente.Segue o nosso guia passo a passo para iniciar a tua jornada no mundo das criptos.Passo 1: cria a tua conta HTXUtiliza o teu e-mail ou número de telefone para te inscreveres numa conta gratuita na HTX.Desfruta de um processo de inscrição sem complicações e desbloqueia todas as funcionalidades.Obter a minha contaPasso 2: vai para Comprar Cripto e escolhe o teu método de pagamentoCartão de crédito/débito: usa o teu visa ou mastercard para comprar Sonic (S) instantaneamente.Saldo: usa os fundos da tua conta HTX para transacionar sem problemas.Terceiros: adicionamos métodos de pagamento populares, como Google Pay e Apple Pay, para aumentar a conveniência.P2P: transaciona diretamente com outros utilizadores na HTX.Mercado de balcão (OTC): oferecemos serviços personalizados e taxas de câmbio competitivas para os traders.Passo 3: armazena teu Sonic (S)Depois de comprar o teu Sonic (S), armazena-o na tua conta HTX.Alternativamente, podes enviá-lo para outro lugar através de transferência blockchain ou usá-lo para transacionar outras criptomoedas.Passo 4: transaciona Sonic (S)Transaciona facilmente Sonic (S) no mercado à vista da HTX.Acede simplesmente à tua conta, seleciona o teu par de trading, executa as tuas transações e monitoriza em tempo real.Oferecemos uma experiência de fácil utilização tanto para principiantes como para traders experientes.
172 Visualizações TotaisPublicado em {updateTime}Atualizado em 2025.03.21