Ethereum Classic Core Developers - Olympia Development Series (Part 1)
Implementing ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112: Base Fee Redirection and the Immutable Treasury
1. Introduction - From Concept to Code
This section provides an overview of the overall architecture of Olympia: its purpose, development history, and how ECIPs 1111-1115 fit into the modular, multi-layer upgrade path. This article will delve into the current engineering practices for two ECIPs, which together define the consensus boundaries of Olympia:
ECIP-1111 — EVM and Protocol Upgrades
ECIP-1112 — Immutable Treasury Contract
These two proposals are the only components in Olympia that modify consensus behavior. Other parts of the framework—governance (ECIP-1113), funding proposals (ECIP-1114), and the optional smoothing mechanism (ECIP-1115)—all operate at the contract layer and do not affect block validity or fork choice. On November 11, 2025, Ethereum Classic core developers initiated the implementation phase, preparing consensus logic and reference client infrastructure for a potential Mordor testnet deployment.
This article outlines:
What ECIP-1111 introduces
How ECIP-1112 defines the treasury target address
How these components work together
What is currently being prototyped in reference client development
This article only describes design proposals and implementation work and does not indicate that they will necessarily be activated or adopted in the future through the ECIP-1000 process. Before deploying the consensus layer changes of ECIP-1111 or ECIP-1112 to Mordor or the mainnet, ETC clients must first verify their stability and compatibility under baseline conditions.
2. ECIP-1111 — Modernizing the Fee Mechanism, Minimizing Network Disruption
ECIP-1111 integrates two widely adopted EVM improvements:
EIP-1559-style fee mechanism (Base Fee + optional tip) This mechanism introduces:
A dynamically adjusting base fee (BASEFEE),
An optional high-priority fee (tip) still paid directly to miners
And a more predictable fee market for modern tools.
2. Support for Type-2 (1559-style) transactions: This functionality has become standard for most wallets and infrastructure.
3. BASEFEE opcode (0x48): This exposes the current block's BASEFEE to contract logic (gas estimators, DEX routers, toolchains, etc.).
What changes for Ethereum Classic (ETC)?
Only one behavior differs from the Ethereum mainnet:
Ethereum Foundation (ETH): BASEFEE is burned.
Ethereum Classic (ETC): BASEFEE is redirected to the treasury defined by ECIP-1112. All other EIP-1559 semantics remain unchanged.
What remains the same?
Miner tips remain unchanged.
Block rewards remain unchanged.
Monetary policy (ECIP-1017) remains unchanged.
Traditional transaction types (Type-0 and Type-1) remain fully valid.
Existing contracts will not break; existing applications require no modifications.
No additional trust assumptions or permission mechanisms are introduced.
ECIP-1111 is additive, minimal, and strictly limited to modernizing the fee mechanism and enabling the BASEFEE redirection function.
3. ECIP-1112 — The Immutable Deterministic Treasury
ECIP-1112 defines the receiving address for the redirected base fees: a minimal, immutable smart contract deployed at a deterministic address. These definitions remain theoretical until client software demonstrates consistent behavior in a multi-client environment, a milestone requiring comprehensive testing to safely assess the Olympia components.
Core Features
Immutability: No upgrade key, no admin, no proxy pattern.
Deterministic address (e.g., via CREATE2): All clients agree on the same treasury destination.
Receive-only upon activation: The treasury can accumulate value but cannot release funds until subsequent governance is activated.
No internal governance logic: Purely a custody layer, not a decision-making layer.
Upon activation (testnet or mainnet):
The treasury can only receive funds.
No withdrawal mechanism is enabled until ECIP-1113 and ECIP-1114 are deployed, audited, and intentionally activated. This separation ensures predictability for consensus upgrades and makes them independent of the implementation of any governance scheme.
4. Clear Consensus Boundaries
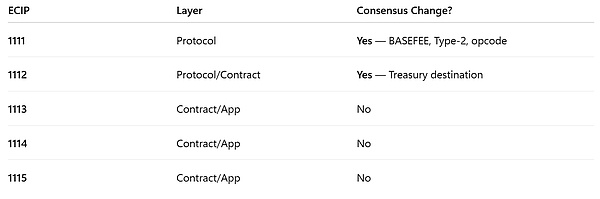
Although Olympia comprises five ECIP proposals, only ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112 change consensus behavior.
Consensus Boundary Summary
ECIP-1111 — Protocol layer. Introduces consensus changes: new base fee mechanism, Type-2 transactions, and the BASEFEE opcode.
ECIP-1112 — Protocol/Contract layer. Introduces consensus changes: defines the deterministic treasury receiving address for redirected base fees.
ECIP-1113 — Contract/Application layer. No consensus changes.
ECIP-1114 — Contract/Application layer. No consensus changes.
ECIP-1115 — Contract/Application layer. No consensus changes.
This modular structure ensures:
Consensus-critical logic remains lean and auditable,
Governance and funding mechanisms can evolve at the contract layer,
Improvements to ECIP-1113 to 1115 require no additional consensus changes.
If adopted, clients implementing ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112 will maintain consensus compatibility, unaffected by subsequent governance layer deployments. Reference implementations can begin prototyping consensus logic during the draft stage, but these changes must undergo comprehensive testing (including baseline client validation such as the Gorgoroth verification described in Part II) before being merged into production clients.
5. Why Governance Activation is Delayed
If ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112 are activated, base fees will begin flowing into the treasury—but treasury spending will remain disabled.
This phased deployment enables:
Independent testing of base fees
Comprehensive auditing of ECIP-1113 and ECIP-1114
Precise coordination among client implementers and infrastructure providers
Predictable behavior for node operators
If governance contracts are subsequently deployed and activated, the treasury will connect with authorized executors entirely at the contract layer (not the consensus layer).
6. Type-2 Transactions and Long-term EVM Interoperability
Type-2 transaction support is crucial for Ethereum Classic to maintain compatibility with:
Modern wallets
Exchanges and custody services
RPC infrastructure
Tooling frameworks (Hardhat, Foundry, etc.)
Block explorers
Cross-chain interoperability
Type-2 transactions do not alter user requirements or introduce permission mechanisms. Traditional transaction types will remain fully supported.
Type-2, as an incremental feature, ensures ETC maintains interoperability with the mainstream transaction format of the EVM ecosystem.
7. The Broader Context — Maintaining a Programmable Proof-of-Work Base Layer
Together, ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112 constitute a foundational step for Ethereum Classic towards a sustainably funded, operational model for programmable proof-of-work—provided the community chooses to adopt these proposals.
These proposals achieve their goals without:
Modifying miner incentives
Introducing inflation
Changing monetary policy
Adding a governance layer to consensus
Altering Ethereum Classic's security assumptions
Their purpose is limited to:
Modernizing the fee market
Establishing a transparent protocol-level value accrual mechanism
If adopted, these changes will pave the way for the contract-layer governance and funding systems in subsequent Olympia proposals, without requiring new consensus rules.
8. Conclusion — Minimal, Secure, and Forward-Compatible
ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112 define the consensus layer components proposed within the Olympia framework. They:
Add Type-2 and base fee mechanisms
Redirect the base fee to a deterministic treasury
Keep all existing user and miner behavior unchanged
Prepare ETC for future contract-layer components
These proposals do not introduce governance logic into the consensus mechanism, nor do they add trust assumptions on top of the existing EIP-1559/EIP-3198 semantics. Their aim is to preserve the conservatism of ETC's core protocol and EVM ecosystem compatibility, while enabling sustainable value flows at the contract layer.
9. ECIP Process Clarity
The Olympia ECIP specifications (1111–1115) are currently in the draft stage and under active discussion. Reference clients have initiated early implementation work on ECIP-1111 and ECIP-1112, which is fully consistent with the provisions of the ECIP-1000 draft stage. Reference implementations will only be considered for mainnet activation after testing on the Mordor testnet is completed. After testnet results are qualified, ECIP proposers may submit specification update proposals. Any decision to advance to "Accepted" status or schedule mainnet activation must undergo community review and the full ECIP-1000 evaluation process. This article outlines the design and implementation work being advanced during the draft stage.
10. What's Next in the Series
With the consensus design framework established, the next installment will focus on the client layer—the Fukuii alpha testing plan is about to launch, aiming to validate ETC client interoperability before Olympia integrations.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute any investment or financial advice. The content is reproduced from EthereumClassic and is for industry information reference only. If you have questions or copyright issues, please contact us for removal.